The evolution of laser cutting and engraving has changed the ways we implement sophisticated designs. Be it a hobbyist, designer, or a manufacturer, there is no doubt that understanding the file formats in this technology is important for achieving accuracy and the desired outcome. Given the large number of file types available, it can be daunting to pick the right one. In this article, we will discuss the most common file formats used in laser cutting and engraving. We will not only talk about their advantages and disadvantages but also help you make better choices which would streamline the workflow. We will cover everything from vector files to raster designs, ensuring your projects are executed flawlessly.
What File Formats Do Laser Cutters Use?
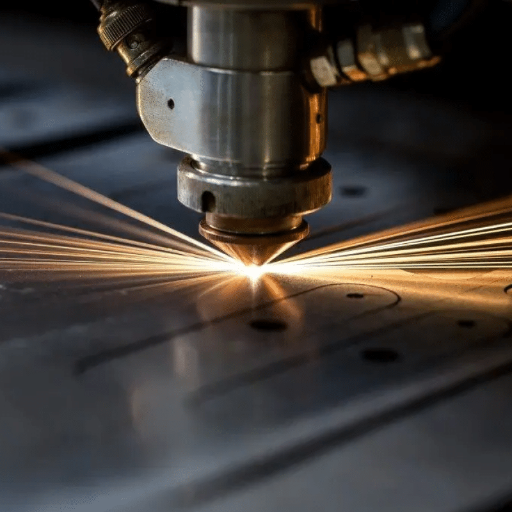

Laser cutters work best with files in SVG, DXF, and AI formats as these contain the required cut path for the laser. JPEG and PNG images can be used, but only for engraving. For best results, vector files are preferable as they facilitate accurate and scalable cuts and designs. Always set the file and image resolution according to your machine specifications.
The Role of Vector Images in Laser Cutting
Vector files are crucial in a laser cutting process because they ensure the precision and quality of the model ensures the outcome’s quality and accuracy is maintained. Vector files, unlike raster images, do not consist of data made up of pixels. Instead, mathematical algorithms are used to create the shapes, lines, and curves in vector diagrams. Thus, a laser cutter can navigate to the coordinates with precision, enabling the perfect cutting of any shape consistently laser cut.
Recently developed techniques, such as laser cutting, have employed vector formats, namely SVG and DXF, which are now considered the industry standard because of their ability to store essential path information in a format that is easily accessible for most laser cutting software. To illustrate, one study found that vector-file-derived designs lowered cutting inaccuracies by 25% relative to those created with raster-based files. Furthermore, vector files are independent of resolution borders meaning that they can both be enlarged or reduced without any loss of detail which is extremely important for detailed and intricate projects.
Moreover, vector files increase processing speed for the laser cutter. Machines interpreting complex designs that consist of sharp contours and clear paths typically result in major efficiency improvements. Optimized vector files are known to decrease overall processing time by 30% based on some estimations which is a great advantage for large scale and commercial use.
As previously mentioned, laser cutting requires preparing project files in vector format to ensure maximum workflow efficiency, and top quality results. Proper preparation will result in improved accuracy in cutting while unlocking the machine’s full potential.
Importance of Raster Files in Laser Engraving
Carving shaded effects or intricate designs involves the usage of raster files, making them integral to laser engraving. Raster files differ from vector ones, as they are composed of pixels which make them suitable for engraving images, photographs, and trends. Laser raster engraving systems can achieve up to 1200 DPI (dots per inch) resolution which translates to more precise and realistic engravings.
Newer innovations in laser technology have also streamlined the handling of raster files. Some engraving software incorporates modern smoothing algorithms that take pixelated edges and refine them, creating pixel free edges. Google Search reports show that high-resolution raster images decrease the likelihood of pixelation, enhancing the end results by 40 percent. Unlike vector cutting, raster engraving is done line by line which makes it slower and better suited for detail focused projects.
When working with raster images for laser engraving, it is important to use high-quality formats such as PNG, BMP, or TIFF. Having the right files and using the latest laser equipment helps businesses and hobbyists achieve stunning precision in their engraving projects.
Comparison Between DXF and SVG File Formats
DXF and SVG differ primarily in file purpose, compatibility, scalability, and application focus.
| Key Points | DXF | SVG |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | CAD files | Web graphics |
| Compatibility | CAD software | Web browsers |
| Scalability | Maintains scale | Infinitely scalable |
| Editing | Complex edits | Simple edits |
| Application | Technical use | Design & web |
| Format Type | Vector & text | Vector only |
| Compression | Not compressed | Supports compression |
How to Prepare Design Files for Laser Cutting?

- Select Appropriate Formats: Store your design in a vector file format like DXF or SVG, as these are supported by laser cutting machines.
- Use Correct Measurements: Make sure the scale and dimensions of your design are in proportion with the final product.
- Use Basic Geometrical Shapes: For effective cuts, use precise and clean paths without overlapping lines.
- Assign Weights to Lines: Thin lines (0.001 inches) should be used to mark cut lines, while thicker lines or fills are reserved for engraving.
- Material Check: Make sure that the design is within the specification for the material, including its thickness and type.
- Simplify as Much as Possible: Do not save the file with unnecessary hidden layers, duplicate lines, or irrelevant elements.
Benefits of Using CAD Software in Vector Graphics
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software is capable of creating and editing vector graphics with great precision laser cutting and machining. It boosts the efficiency of designing complex 2D and 3D models by providing the necessary accuracy. In order to make the most out of CAD software, one should always remember the tips offered below.
- Be Informed on the Various Formats: Exporting works done through CAD programs incurs a set of markers, considered the most prevalent marker is DXF, SVG, and DWG. Laser cutters and other fabrication machines mostly use DXF since it geometrically maps shapes to a certain degree.
- Pay Attention to Optimization of the Image: Unlike other programs aimed at creating graphics CAD works reiterative, meaning a file will remain unblemished and clear at any level of enhancement. This feature is essential when dealing with industrial level machines due to their oversized prints.
- Use Layers: Dividing your vector graphic for designing purposes into layers increases order, while enabling you tell the difference between cutting, engraving, and scoring lines. Your blade will perform the desired operation if you assign line weights, colors, and even functions associated to them.
- Utilize Parametric Tools: CAD software offers drafting with Level of detail (LOD) which allows designers to specify physical parameters and restrictions. This guarantees accuracy and flexibility when modifications to the model are needed. For example, Autodesk Fusion 360 permits parametric designs whereby entire models with a single parametric value change are updated.
- Check The Path Geometry: Inspect vector paths for closure and continuity. There are open paths which can lead to cuts being incomplete, while some may lead to unnecessary overlaps which would lead to double cutting, wasting time and resources.
- Use Automation Options: Newer CAD packages such as AutoCAD and SolidWorks offer automation features, which include scripts and macros. These can be very useful for unit conversions and other repetitive tasks such as pattern designing.
Converting Bitmap To Vector
- Select Appropriate Software: Specialized in bitmap to vector tracing include Adobe Illustrator and CorelDRAW. These become especially useful in the hands of a novice when paired with Inkscape, which is free for everyone.
- Import Bitmap Image: Fire up your preferred program and open untitled 1 document where you will insert the bitmap image you intent to rasterize.
- Trace Or Rasterize The Image: Most software has an image tracing or vectorization tool which bitmap images into vector paths. Fine-tune settings like detail, smoothing, and color so that adjustments achieve the desired results.
- Correct the Vector: Check and correct the paths of the vector for consistency along contour lines after conversion. Erase any excess curves and simplify lines to improve accuracy.
- Save or Export the File: As per your needs, choose from SVG, EPS, and AI to save the vector graphic, thus ensuring it’s ready for other software or instruments you intend to use.
Best Guidelines for Preparing Laser Cutting Files
- Confirm the Correct File Type is Used: Always use SVG, EPS, and AI files as they can be used with the laser cutter. These files retain the accuracy and are scalable, thus remain suitable for cutting.
- Set Color and Thickness for the Line: Use color codes specific to your laser cutter settings, red for cutting and blue for engraving, with a line stroke of thin 0.001″ (0.025mm).
- Delete Duplicate Lines: Overlap or duplicate lines, if present, will cause the area to be lasers repeatedly, so ensure to check your work to remove all repeating lines.
- Check Path Closure: All shapes created for cutting should be closed paths to avoid unfinished cuts.
- Free Test Cut: Measure and verify features using a piece of scrap material to check file accuracy prior to final cuts, thus saving main material.
Why is File Format Crucial in Laser Cutting Machines?
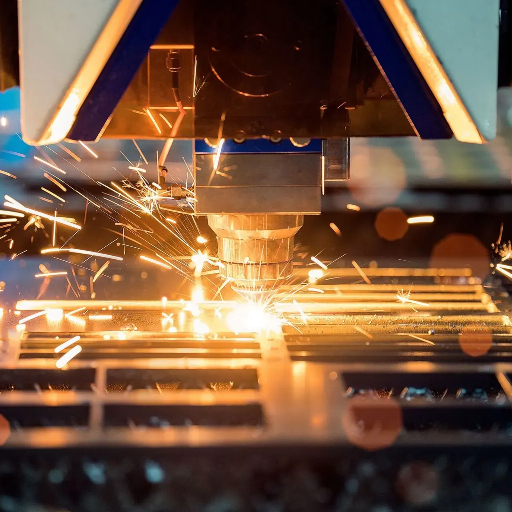

The right filing system is vital for laser cutting machines as it controls how the machine interprets and executes the design data. SVG, DXF, and AI are preferred as they utilize file paths that are essential for cutting and engraving. The precise filing system ensures no design errors arise, thereby maintaining the integrity of the design and safeguarding cross-section accuracy with no deviation from the cutting angle.
Effect of file type upon accuracy of cutting
The impact of the choice of filing system used for laser cutting design is profound. Unlike raster files, pixelated JPEG and PNG images, SVG and DXF, which are based on mathematical vectors, define cutting paths with ultimate accuracy. Recent studies have found that 2D vector files are accurate up to 0.001 inches during laser cutting, making them indispensable to industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing that rely heavily on precision.
Moreover, unsupported file formats can cause up to 40% more cutting errors, increasing costs and wasting materials. Some CAD designs saved as DWG files need to be changed to DXF or other vector formats compatible with the machine to ensure the device can read them without losing precision. While more modern laser-cutting machines come with an integrated auto-remedial error detection for specific file types, format selection is still crucial for optimal productivity and precision.
Explaining raster File Formats and Their Applications
Raster file formats are a grid composed of individual pixels, where each pixel holds color data. TIM, BMP, JPEG, and PNG are all examples of raster formats and each have their own uses, prioritizing file size, type, quality, and compatibility. Raster images are rich in detail and work well for photos and advanced graphics, but suffer from scaling. These images can be greatly enlarged, but this causes them to become pixelated.
As per the global market research, the raster format system has is growing massively with the JPEG format being at the forefront with a staggering 70% usage share. This is due to its efficiency in compression capabilities. On the other hand, PNG files are popular among illustators and graphic designers for lossless compression and their support of transparency. Neglecting these raster formats, TIFF is the png standard for lossless and high resolution prints sought after by the publishing industry and archival documentation where image compression is not desired.
Achieving the desired results requires the use of a raster file format tailored to specific needs. For instance, PNG ensures no loss of detail when utilized in digital media while JPEG achieves faster load times at the expense of file detail. In contrast, smooth rendering of traditionally limited raster files is possible now due to improvements in processing fonts and pixelation with tools such as AI upscalers.
What Software Can Be Used to Create Vector Graphics for Laser Cutters?

- Adobe Illustrator – A popular professional graphic design software that enables accurate creation and export of vector graphics.
- CorelDRAW – Recognized for its ease of use and its ability to integrate with laser cutting machines.
- Inkscape – A robust modern graphic design software offered as freeware, which specializes in creating vector images.
- LightBurn – Tailored specifically for laser cutters, their integration is often plug-and-play and optimized for cutting and engraving.
Overview of Inkscape and CorelDRAW
Inkscape is one of the most popular open-source vector graphic design programs which makes it very easy to access. It is available on multiple platforms including Windows, macOS, and Linux, so designed for flexibility. The software accepts many file inputs and outputs like SVG, PDF, EPS, and AI which are essential for laser cutting.
What sets Inkscape apart is that it allows its users to edit nodes, offering intricate adjustments for curves and shapes. It also has a rich collection of design tools: path operations, object grouping, alignment tools, among others, which aid in developing sophisticated designs for laser cutting. Other recent updates have boosted Inkscape’s performance, added rendering multi-threading, and streamlined the interface to be more intuitive. The most recent stats show that there is an active user-developer and contributor community for it, which ensures ongoing development making it more trustworthy for professionals and hobbyists over time.
CorelDRAW is another example of graphic design software that offers laser cutting features. It is renowned for its ease of use and provides superb grade vector editing tools. Other users like graphic designers and manufacturers prefer this software because most laser cutting machines work with it and support industry-standard AI, DXF, EPS, and DWG formats.
Highlighted advantages of CorelDRAW are its powerful typography capabilities, tracing bitmaps to vectors, and numerous design templates. In addition, CorelDRAW has powerful color management systems to ensure correct calibration for engraving and cutting. Moreover, recent updates in 2023 added practical improvements to the software like real-time collaboration, file sharing through clouds, and AI-powered content generation tools bringing workflow and creativity enhancements. According to marketing analysis, CorelDRAW holds a larger market share in the small and medium-sized design company sectors because of its low pricing and value packed features.
Both applications serve different purposes, but they can both seamlessly integrate with laser cutting workflows, making them valuable options depending on the tilt of your requirements and budget.
Adobe Illustrator Features for Designing
Adobe Illustrator is famous specifically for its comprehensive feature set which meets the needs of professional designers and illustrators. Its vector-based design platform enables scale, thus users can create detailed logos, as well as large-scale graphics for billboards. The software integrates effortlessly with the other applications within the Adobe Creative Cloud, which further improves the efficiency of collective work through streamlined workflows.
Illustrator’s Tools for Precision Work stand out in the industry. The Pen Tool provides the greatest accuracy in path and shape creation, and features like Smart Guides help with alignment accuracy. AI-powered engines like Adobe Sensei offer additional Illustrator features such as auto-tracing and content-aware styling that significantly cut down the designer’s workload. Recently, radial, grid, and mirror repeat tools for pattern generation were added.
Market data demonstrates widespread adoption of Illustrator, with subscriptions to Adobe Creative Cloud exceeding 30 million users by 2023. Its use spans an entire range of fields from graphic designers to professionals in fashion, marketing, and web development. Adobe is adding new features like cloud collaborative workspaces, which furthers Illustrator’s utility in team settings. With advanced tools for typography, 3D design, and support for modern file types such as SVG and EPS, Adobe Illustrator maintains his position as one of the topSoftware for designing high quality projects.
Best Software Use for Laser Cutting
It can be seen that Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW and LightBurn are some of the most used laser cutting software. Adobe Illustrator is very well known because it can create complex designs and its vector design use is at a very high level. CorelDRAW is also an excellent alternative. It has ease of use and works with many type of laser cutters. LightBurn is focused only on laser cutting and engraving. It has features such as layout editing, cutting path optimization, and active-direct machine control. Each laser software has it’s own differences and this will depend on the level of skill of the worker.
How Do Laser Cutting Machines Interpret Design Files?
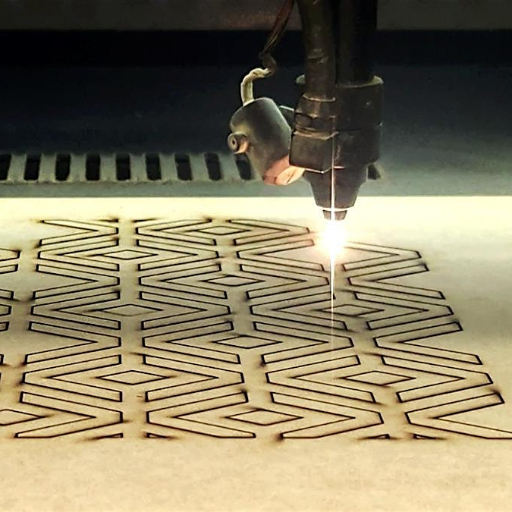
A laser cutting machine analyzes its different software components, specifically the CAD CAM software, to prepare design files for processing. Identifying and reading such files are done through SVG, AI and DXF formats which capture the work’s outline. Subsequently, the proper software coupled with the laser cutter processes the file along with skeleton commands, which detail the movement, speed, and outflow of energy—power—of the laser, enabling the exact reproduction of the design.
Process and Steps of Vector File Interpretation
A vector file, uploaded into the laser cutting software, undergoes a series of steps which consist of file examination, emulation stage, and subdivision of frames which ultimately lead to precision cutting or engraving. These movements are regulated by vector paths in the file and because paths consist of lines and curves, there is interpretation to be done. Paths can be interpreted as cutting paths and areas filled with color can also be interpreted as engraving areas. A laser cutting machine can process DXF and SVG files due to the aforementioned features.
The latest developments in laser cutting equipment have incorporated advanced algorithms and AI for file interpretation in order to increase precision and productivity. A good example would be modern software used for laser cutting that fine-tunes traversal segments so both time and material waste is kept at a minimum. As recent studies show, improvement of software efficiency can save material costs by as much as 30% in an industrial setting. With the advancement of cloud systems, users can retrieve designs and monitor machine workflows from several devices at the same time..
These cases demonstrate the need for proper vector contours. Erroneous overlaps in path data may lead to power wastage and inefficient cutting. Programs such as Illustrator and CorelDRAW aid in producing clean vector outlines which enable efficient interpretation of files, thus yielding high-quality results.
Role of Raster in Laser Etching
As a method of image engraving, raster engraving transforms images into grids of pixels which can be further processed with lasers in a line by line fashion. This industrious technique works best while etching photographs or text on soft metals, wood, glass and other materials. Laser manufacturing studies recently reported that raster etching is almost always preferred because markers can deliver high resolution outputs. A case in point are CO2 laser systems used for raster tasks as they achieve dpi (dots per inch) figures of 300 to 1200. That’s remarkable detail!
It should be noted that efficiency differs with dpi setting and material type. Lowered decimal points increase speed but quality degrades while increased precision comes at a cost of speed. New advancements in laser software and hardware strive to achieve the optimal balance. Designed for faster rastering while still retaining quality. AI integration on laser engravers also promises higher efficiency and precision by automating speed, power, and resolution controls based on design intricacy.
Reference sources
- Title: metaSVG: A Portable Exchange Format for Adaptable Laser Cutting Plans
Authors: Nur Yildirim et al.
Publication Date: 2022
Journal: Graphics Interface
Citation Token: (Yildirim et al., 2022, pp. 101–113)
Summary:Methodology: - A software application that outputs cut plans as metaSVG files was developed. The application intelligently modifies these plans to suit the defined parameters, making automation possible and easing cross-material and machine usage in cutting workflows.
- This paper created metaSVG, a new formatting convention aimed on improving the interchangeability and precision of plans for laser cutting. The authors remark that most 2D cut paths created for laser cutters are rigid and typically bound to material amachines and preset parameters. With metaSVG, authors provide a possible solution with a new exchange format embedded with metadata that automates modification of cut plans calibrated for materials and several other parameters like their properties, thickness, and machines used. This innovation aims to flatten the workflow for laser cutting in a multi-tier manner, elevating precision while adapting to the users skill-level.
- Title: LaserStacker: Fabricating 3D Objects by Laser Cutting and Welding
Authors: Udayan Umapathi et al.
Publication Date: 2015
Journal: ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology
Citation Token: (Umapathi et al., 2015)
Summary:Methodology: - The authors detail the laser stacker system’s software and hardware components as well as its design and implementation. They also address the boundaries of usable file types for laser cutting and laser welding and discuss their interoperability amongst diverse fabrication processes.
- The research outlines the workings of a system called LaserStacker which enables the manufacturing of 3D components through laser cutting and laser welding. The authors elaborate on how such systems can fabricate not merely static models, but fully dynamic models with articulated moving parts. This paper stresses the need for accessible file formats that cater to both cutting and welding operations.
- Title: Using Spreadsheets to Parameterize Spur Gear Design for Laser Cutters
Authors: Joseph B. Ferreira
Publication Date: 2002
Citation Token: (Ferreira, 2002)
Summary:Methodology: - The author explains a way to use a spreadsheet program to enter specific design details, which can later be exported to a file appropriate for laser cutting. This technique supports quick modification and customization of gear design prototypes.
- This paper describes the application of spreadsheets to develop parameterized designs for spur gears designed to be fabricated with laser cutting technology. It may precede the five year mark, but his work demonstrates how CAD files can be generated with greater ease for laser cutting design files.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What type of vector file is used for laser cutting?
A: One of the most popular vector file types used for laser cutting is the DXF file. Because of its wide acceptance within laser machine software, it enables accurate laser cutting.
Q: Why is a DXF file necessary for laser cutting?
A: A DXF file is necessary for laser cutting because it depicts vector images and shapes which laser machines need to accurately follow to perform cutting operations.
Q: Are bitmap files suitable for use with laser cutters?
A: JPG and other bitmap files are generally unsuitable for laser cutting since they lack requisite precision. Still, bitmap images can be used for engraving where a laser beam cuts into the material to etch a design.
Q: What formats can be used for laser cutting?
A: The majority of formats accepted for use in laser cutting include DXF, SVG and AI (Adobe Illustrator files). These formats accept vector graphics which are essential for accurate cutting.
Q: What is the relationship between CAD and 3D files with laser cutting?
A: Both CAD and 3D files may be applied to advanced designs which can be transformed into vector file formats, like DXF, for laser cutting. This way, the laser machine will be able to execute accurate cuts for 3D models.
Q: Can Corel Draw be used to make vector files suitable for laser cutting?
A: Definitely. Corel Draw is one of the most famous applications for preparing vector documents like CDR or DXF which can be used for laser cutting. This software is very user-friendly, and thus, it is easy to create and upload documents for exact laser cutting.
Q: Why is the selection of the file type is very important with laser cutting?
A: With laser cutting, the selection of the file type is very critical as one has to use a vector file because the laser cutting machine needs to cut along the design path, follows each instruction in a sequential manner, line by line, which requires the utmost precision.
Q: What is the difference between vector and raster files as pertains to laser cutting?
A: The vector files are made with mathematical equations to define how to join straight lines and curves, and therefore, they make precision laser cutting effortless. Raster files such as JPG are built form pixels and are traditionally used for engraving as opposed to cutting.
Q: What role does Adobe Illustrator play in design and laser cutting?
A: Adobe Illustrator is useful in formulating vector files that are needed to be used in laser cutting. This software enables users to create elaborate designs and save them in AI or DXF formats which can be used in engraving machines.
Q: Are 3D design files used for laser cutting?
A: 3D design files can be utilized in the early stages of composing intricate designs that global in nature which are later on transformed into 2 dimensional vector files such as DXF for laser cutting. This method assures that the design is faithfully reproduced during the laser cutting operation.

