Mobile welding has emerged as a critical capability in welding, especially in construction, maritime industries, and freight, offering unparalleled convenience, effectiveness, and practicality, especially soldered on the spot. The purpose of this article is to lay out the tools, techniques, and methods of portable welding. From welding machines and welding guns to material safety and compatibility considerations, we strive to inform professionals and hobbyists which knowledge suffices to elevate their craft. This guide, whether you are a skilled welder or just starting out, aims to enhance your skills and understanding of portable welding in any work setting.
What is Portable Welding and How Does it Work?
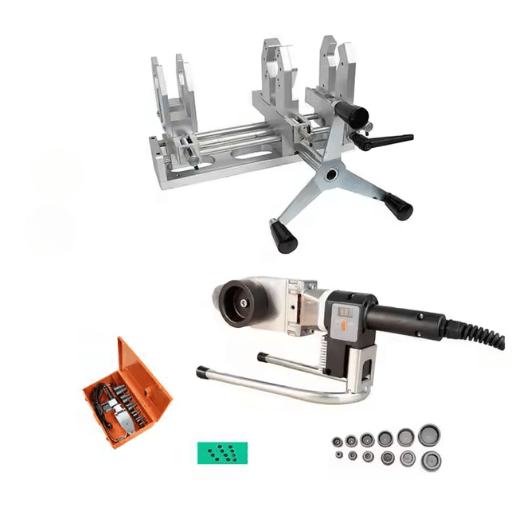
Portable welding is defined as executing welding processes with the aid of portable welding tools and equipment. It allows welders to perform work in a remote location, on-site or confined area where conventional stationary welding machines cannot be set up. Portable welding usually includes small and lightweight welding machines which run on electricity, fuel, or battery-operated systems, providing greater flexibility. The process of welding entails heating metal parts to their melting point to fuse them together—MIG, TIG, and stick welding are the most popular methods. The mobility of the equipment fosters adaptability across diverse sectors, such as construction, automotive servicing, and pipeline servicing.
Portable Welding Fundamentals Overview
The evolution of portable welding equipment has positively impacted the productivity and accessibility of metalworking in different industries. Welding technology advancements have driven considerable growth in the industry. Reports estimate the worth of global welding equipment to be approximately $13.4 billion in 2022, portable welding solutions capturing a large portion of that as demand expands. The available lightweight welding machines that range from 15 to 25 pounds have contributed to easing the logistical burdens associated with on-site welding, improving workplace agility and convenience.
One of the most recognized uses is in construction, where portable welders allow structural component fabrication to be completed in a timely manner and with minimal downtime. Equally, in the vehicle auto repar industry, on-site welding has lowered vehicle repair retunr times and costs. Pipeline maintenance crews working in remote or difficult locations heavily depend on portable welding tools to ensure that they can perform routine maintenance and troubleshoot equipment problems.
A modern portable welder can often support multiple processes such as MIG gas metal arc welding—used for high-speed applications—TIG gas tungsten arc welding, which is more precise, and stick welding for extreme conditions. These machines can operate from 20 amps for delicate tasks to over 250 amps for heavy-duty jobs, demonstrating flexibility to meet diverse project requirements.
Applications of Welding Equipment: the Mobile Welder in Metalworking
Understanding the specifications and features of portable welders helps explain what they can do:
- Minimum Output: 20 Amps (welding of more fragile materials such as aluminum sheets).
- Maximum Output: 250+ Amps (structural steel works and other heavy-duty welding tasks).
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas)
- Best suited for tasks requiring great speed and control over material thickness.
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas)
- Involves more precision work, mostly with stainless steel and other non-ferrous materials.
- Stick Welding (SMAW)
- Best Welding method for harsh weather conditions and outdoor use with mixed surfaces.
- 120V for standard household sockets.
- 240V for industrial-grade power usage.
- Dual voltage for better adaptability at different sites.
- Flexible weight: 20 to 60 lbs. depending on the model and additional features.
- Equipped with carrying handles and/or wheels for better mobility.
- Digital adjustment for better precision.
- Overhead modes for standard parts and materials.
- Durable construction improves machine life.
- Remote generators make working in the field easier.
- Fitted compartments reduce clutter.
The above list exemplifies the diversity modern portable welders possess in addition to their technical versatility, which meets various needs and demands in metal fabrication.
The Advantages of a Portable Welding Machine
Welding and metal fabrication work has been made easier by portable welding machines since they brought about tremendous efficiency. The primary objective of those machines is to improve productivity without compromising quality, which they certainly achieve with remarkable power. Listed below are the rest of the supporting technical specifications and data points:
Power Output Range: The majority of portable welders have polymorphic output ranging with the parameter of 20 to 250 amps. This means a variety of welding tasks can be accomplished: from welding thin sheet metals to thick steel plates.
Input Voltage Flexibility: The convenience of Dual-voltage input (120V/240V) makes the machines usable in many electrical surroundings that include both home and industrial environments.
Weighted Portability: The most advanced designs place the weight at 25-35 lbs. which allows easy transport without sacrificing function.
Warranty and Supportable Policies: It is no surprise that modern machines are computerized as it gives them greater reliability. A wide variety of such machines have an estimated efficiency rating exceeding 85 percent which in turn brings down the running costs.
These aspects according to the data available has boosted the effectiveness of portable welding machines for professionals and hobbyists seeking for precision, mobility and dependability in their work.
How to Choose the Right Portable Welder for Your Needs?

Scope: Specification and Output
Reviewing a welder’s specifications and outputs is crucial for meeting the application requirements while selecting a portable welder. Below are some critical considerations and available data which need evaluation:
- Scope: Specification and Output
- Voltage Range: Flexibility their need includes options like 120V, 240V or dual voltage.
- Frequency: 50/60Hz is common according to prevailing regional standards.
- Output Range: Providing adequate amperage above the material thickness would be welded. For welding thin materials 30-50Amps would work whereas over thicker materials 200Amps or more would be needed.
- The duty cycle of a welder defines the percentage of 10 minutes the machine could run without overheating. For example; if the machine had a 60% duty cycle at 150A then it would be able to run six minutes continuously before needing four minutes to cool off.
- MIG (Metal Inert Gas)
- TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas)
- Increased compatibility broadens versatility for different types of applications.
- Weight: Generally, compact units range between 20 and 50 lbs.
- Dimensions: Enhanced maneuverability is one of the benefits smaller size provides especially in confined areas.
- Handle or Wheels: Ergonomic design makes for easy transport.
- Metals Supported: Depending on the project requirements ensure the machine can work with steel, stainless steel, aluminum or cast iron.
- Efficiency Rating: Numerous models guarantee lower expenditure due to reduced power consumption and achieving efficiency levels over 85% for almost all models.
- LCD Screens or Digital Displays ensure careful regulation of parameters.
- Automatic Thermal Overload Protection improves safety measures.
- Ground clamps, welding torches, and consumable kits are among the Included Accessories.
Users have the power to make decisions after considering all specifications which allows selecting the most appropriate portable welder for desired tasks and financial constraints.
MIG, TIG, and Stick Welders Comparison
Analyzing MIG, TIG and Stick welders, it is easy to notice that each process has its own unique set of strengths designed especially for different users and skill sets:
MIG Welding: It is the most straightforward type of welding, making it the go-to choice for fast-paced environments. Automated wire electrode feeding helps with welding thin to medium-thick steels and aluminums. Like all welders, MIG welders need shielding gas but spatter-free welds are a guarantee.
TIG Welding: Of all welding methods, this possesses the utmost level of accuracy. Thin stainless steel and some exotic metals can be intricately welded, which makes this method popular among artists. Clean and visually appealing welds can be achieved with a non-consumable tungsten electrode. This method requires a lot of time and skill though.
Stick Welding: Designed for colder and harsher environments, Stick welders perform well without the need for a shielding gas. This makes them ideal for thicker materials that have rust, dirt, or other contaminants. While heaving some spatter and not being as beginner-friendly, Stick welding is ideal for structural applications requiring strong, durable welds.
Choosing the right welding method depends on the project at hand, the materials involved, and the operator’s skillset. Every process caters to different industries and has different outcomes, which creates versatility for use in many fields.
Essential Protective Equipment and Voltage
In welding, the importance of voltage cannot be stressed enough since it affects the stability of the arc, the penetration, and the quality of the weld. Different welding processes also have their preferred voltages, such as MIG welding which uses around 15-25 volts, or Stick welding which relies on higher voltages between 20 to 30 volts depending on the electrode and material used. Maintaining balance in setting the voltage helps eliminate defects like undercutting and incomplete fusion, which strengthens the integrity of the weld.
Also PPE, or personal protective equipment. It also provides shields for things like debris, a heat, radiation etc. OSHA states that welding helmets with a shade filter of appropriate 8-13 for the varying degrees of welding techniques, flame resistant gloves, and sturdy welding jackets are all pieces of PPE for welding work. Having proper PPE reduces workplace injuries, on utilizing the correct proportions, by as high as 50 along with lower fostering the practice of safety welfare practiced in a welding area.
What Are the Key Components of a Portable Welding Setup?
Analyzing the Portable Welding Gun
The versatile portable welding system allows a welder to operate in diverse locations while ensuring both safety and performance. The list below offers insights into the specific components needed to construct a simple portable welding system.
- Easy to carry due to its compact size and light weight.
- Suitable for different practices due to adjustable amperage.
- Enhanced versatility from AC or DC power sources.
- Comfortable during long jobs due to the ergonomic handle.
- Highly durable trigger control offers precise welding control.
- Provides adequate amount of shielding gas (for MIG/TIG processes) to increase weld stability.Gasoline, diesel, or battery powered machines can be used for operating a generator at a remote site.
- Maintains constant voltage output for reliable arc operations.
- Filled with the necessary gas components, which may include argon, carbon dioxide or other mixtures.
- Equipped with a gas pressure and flow measurement instrument.
- Appropriate electrodes for Stick (SMAW), MIG, or TIG welding as per the designated work.
- Filler rods or wire that leads to strong and non-defective welds.
- Grounding cable used must be heavy duty for safety and completing the electric circuit.
- Rugged and insulated welding leads because it can be subject to abrasion and damage.
- Stable positioners to firmly grip the workpieces to the welding fixture.
- Adjustable clamps for different dimensions of workpieces.
- Personal protective equipment (e.g. helmets, gloves, jackets for welding).
- Fire resistant blankets to contain the spark in the area.
- Tools like pliers, wire brush, chipping hammers for cleaning or adjusting are also essential.
- Extra spare consumables like contact tips, nozzles, and drive rolls for instant exchange.
- Small exhaust or fume fans for the confined or remote areas to improve air quality.
All of these components are very important in achieving a portable welding device that is safe and fast. Maintenance as well as periodic check-ups is recommended for these equipment to ensure reliability and durability.
The Function of Inverters and Generators
An amalgam of inverters and generators is key for a mobile welding system due to it pavsing the necessary electric power for its proper functionality. Generators are responsible for transforming mechanical energy into electrical energy that fuels a welding tool in places where electric wiring is absent. These devices come is different sizes; the nominal power of the unit is given in kilowatts (kW). Some are small as 2-5 kW while others may exceed 10 kW and are used for heavy duties.
On the other hand, welding inverters are of extreme importance in the control of working power for the welding machine. Due to the sophisticated electronic devices it uses, the inverter is able to turn the incoming power to high frequency DC electricity and thus provide better control on the welding. The modern power supply systems that employ transformers often use much more bulk and weight than inverters which set off one their distinct advantages, in addition to their needing less energy than other power systems, emitting about 85% overall. In portable systems, inverters’ weight and power efficiency become essential thus making their widespread utilization paramount.
In choosing an inverter or a generator for portable welding, factors such as the process of welding which includes MIG, TIG, Stick, power levels, duty cycle, and the environment need to be optimal and reliable. As an example, some MIG welding generators need to serve a minimum of 5-6 kW and TIG welding needs smoother power and better inverter precision for stable arcs. Regular maintenance like checking fuel, replacing oil, and clean air filters enhances the effectiveness and operational life of these parts.
Key Accessories: Welding Rods and Headgear
When gearing up for welding operations, it is crucial to plan the respective accessories and equipment to promote safety, precision, and top-notch results. Here is a comprehensive list of accessories for welding and their purposes:
Protect the welder’s skin and eyes from harmful radiation such as UV and IR.
Auto-darkening models are suggested for better comfort and ease of use.
Also termed as electrodes, these items come in numbers of forms like E6010, E6011, and E7018. Each one fits a specific metal and has its unique purpose.
Always check that they are suitable with the method of welding being applied.
Sparks, burns, and sharp objects are a danger that need to be defended against with heat proof gloves.
For MIG and TIG hand welding, heavy-duty leather gloves are the best option.
Flame retardant welding jackets, aprons, and sleeves protect the welder from sparks, spatter, and intense heat.
Durable leather and treated cotton are the norm.
To offer extra eye protection when grinding or cutting, these are worn under the helmet.
Ground clamps provide attachment to a reference point of the same potential to have a reliable electrical connection.
With manual arc welding, electrode holders assist in controlling the arc better.
An important activity to achieve high quality welds is cleaning them to remove applicable slag.
Cleaning surfaces to remove weld joints prior to welding is another activity required to maintain a neat appearance and functional surfaces.
This gives limited shielding to nearby personnel against arc flash but permits the operator to see.
Instruments like tape measures, markings, and squares guarantee precision in joint preparation and alignment.
Welding generates dangerous gases and particles that are blocked by the masks and respirators.
Overheating and equipment damage can be prevented using cooling fans or liquid-cooled torches, which maintain the equipment at operational temperatures.
The combination of all these tools and accessories aids in optimal safety and performance during the welding operation.
How to Use a Portable Welding Machine Safely?

Welding Safety Guidelines
Always wear protective goggles and the appropriate auto-darkening welding helmets to guard against intense light and arc flash. Cropped sleeves should be worn with gloves while performing welding tasks, but the fabric must be resistant to fire. OSHA mandates that welding helmets provide proper eye protection in compliance with ANSI Z87.1 standards.
Welding processes release hazardous and toxic gases consisting of metals and dangerous compounds. Use of ventilators or exhaust hoods greatly reduces the concentration of toxic fumes. According to the American Welding Society (AWS), local exhaust ventilation has been shown to significantly reduce harmful fume concentration by up to 90%.
Routine checks on cables, electrodes, and torches should be performed prior to commencing any welding task to mitigate possible failures and hazards due to worn parts. Research indicates that unmaintained apparatuses contribute to almost 20% of the industrial welding accidents.
Housekeeping should be performed to eliminate any combustible items from the immediate vicinity of the welding zone. Reports estimate that adopting appropriate housekeeping measures can minimize workplace hazards by 25%.
Portable welding machines are designed to operate at extremely high currents which increase the risk of electric shock. Operators must wear insulated gloves and check grounding connections in addition to proper glove placement. Guidelines from the National Safety Council suggest the further use of Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) to enhance safety for equipment operators.
Following these principles of safety fosters a professional welding environment because it mitigates risk while complying with industry requirements.
Using Protective Equipment Effectively
Proper protective equipment must be worn to ensure the safety of personnel while operating portable welding machines. Recommended Equipment and their Purpose are outlined below:
Prevents exposure of eyes and face to harmful Ultra Violet/Infrared radiation (UV/IR), intense light, and flying sparks. Visibility during setup and welding is provided by the auto-darkening feature.
Provides protection from high temperatures, electric shock, and sharp metal edges. Ensuring gloves are fire-retardant and tailored for dexterity in the fit is crucial.
Items that envelop the body to prevent burns inflicted by sparks, hot metal, and UV radiation. Garments should be composed of treated cotton or leather.
Prevents foot injuries associated with falling objects, sharp debris, and even electrical danger. The shoes must have good quality, non-slip soles for optimum grip.
Respiratory Protection:
Welding related materials are the source of dangerous fumes that need to be filtered. Properly rated respirators such as N95 masks or powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs) should be used according to the type of work to be performed.
Hearing Protection:
Reduces the chances of incurring hearing damage due to the noise generated by the welding tools over an extended period of time.
Protective Eyewear or Goggles:
Offers supplementary eye protection whilst grinding or preforming processes on the material where sparks or some form of debris are present.
All of the safety wear must comply with the relevant operating and industrial safety standards such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). This equipment must also undergo routine checkups and servicing to maximize safety and performance.
Achieving Accuracy in Welding Assignments.
Achieving a high quality weld joint requires precision which means a number of steps must be followed to ensure that the joint lasts long enough to be cost effective and meets the standards of the industry. This requires a good amount of attention to, at the very least, the type of materials that are used, the method of welding, and the environment in which the welding will take place. As an illustration, there is evidence to support that some environmental attributes such as the surrounding temperature and humidity can have a considerable impact on the well. As detailed in research found in the Journal of Materials Processing Technology, welds witness a sharp uptick in humidity-laden settings where contaminants are elevated on the base and filler materials, incurring a defect rate increase of upwards of 25%.
As previously mentioned, accuracy is improved with more modern welding methods like robotic welding and laser welding systems. An industry report states that use of automated systems has been shown to reduce dimensional errors by as much as 60% when compared to manual welding as precision and consistency are more accurate and dependable with automation. The precision of calibration and other tailored settings also matters a lot to welding as misaligned tools can lead to wrong weld bead profile which affects the strength and fatigue resistance of the joint in welds.
Quality control that includes the visual level, ultrasonic, and X-ray inspections guarantees that the welds thought to be done meet the codes as standards such as AWS D1.1 and ISO 3834. Inspections performed including recording data increases confidence in the processes done and enhances the traceability of the processes done in welding.
What Are Some Common Applications of Portable Welding?

Portable Welding in Automotive Repair
As for automotive repair, welding done professionally serves numerous purposes; it helps repair mechanical frames, exhausts, and other parts of the vehicle structure. Portable welding offers the mechanical engineer an option for ease, since it can be executed on-site. The major types of welding include MIG, TIG, and MIG welding, which all use metals including steel and aluminum. Sometimes expensive and time consuming to transport in pieces, this alternative reduces the amount of time in the shop and the amount of money spent. With the introduction of new technologies and tools such as the light-weight inverter based systems, portable automotive repairs can now be done with higher precision, efficiency, and complex capabilities.
Metal Fabrication and Construction Uses
Fabrication as well as the construction industry make use of welding technology and its advancement over the years. The same features also state that the global market for welding products had an estimated $13.6 billion in 2021, and an annual growth rate of 4.3% is expected between the years 2022 to 2030. These jobs require the use of MIG, TIG, and arc welding methods for accurate shaping and joining of the structural components of a given piece. A good example is the structural steel welding which commonly uses flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) because it does well with thicker materials and harsh environments. Also, automated welding construction systems have cut costs by 30% since they were first introduced to construction projects, speeding up production while still ensuring projects are completed within the deadlines whilst keeping the necessary safety standards and quality control checks.
Crafting and DIY Welding Projects
With the opportunity to use welding for DIY tasks, one can come up with unique ways to customize or make tools that are guaranteed to withstand the test of time. This is also useful in repairing metal tools, and fabricating furniture pieces, among other things. Learning welding basics offers a lot of freedom to hobbyists as they do not have to depend on mass manufactured products which are costly and lessen the value of creativity.
Reference Sources
1. Design and Development of a Portable Resistance Spot Welding Machine for Small-Scale Industries
- Authors: Kaushal Jha et al.
- Published In: Applied Mechanics and Materials
- Publication Date: February 5, 2024
- Citation Token: (Jha et al., 2024, pp. 97–105)
- Summary:
- This study presents the design and development of a portable resistance spot welding (RSW) machine aimed at small-scale industries. The machine features a copper electrode with a diameter of 0.394 inches and a length of 10 inches, powered by a transformer with specifications of 6 V-1500 A and 7 variable current settings.
- Key Findings:
- The machine is cost-effective, with a development cost of only 6100 rupees.
- It is capable of reliably welding two 3 mm mild steel plates under various current, resistivity, and voltage settings.
- The design is compact, lightweight, and user-friendly, making it suitable for diverse welding applications, especially in remote locations.
2. Portable VR Welding Simulator
- Authors: Dariusz Michalak et al.
- Published In: Applied Sciences
- Publication Date: August 30, 2024
- Citation Token: (Michalak et al., 2024)
- Summary:
- This paper discusses the development of a portable virtual reality (VR) welding simulator designed to aid practical training in MIG/MAG welding. The simulator utilizes an off-the-shelf mobile VR set, a welding torch, and 3D-printed welding coupons.
- Key Findings:
- The simulator was found to be a useful training aid for welders, justifying further development and integration into educational and training programs.
- It allows for varying levels of immersion, making it suitable for users prone to cybersickness.
3. Portable Tack Welding Device
- Author: Stephen Bascos
- Published In: International Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences
- Publication Year: 2024
- Citation Token: (Bascos, 2024)
- Summary:
- This study focuses on the development of a portable electronic tack welding device, evaluating its tacking time duration, power consumption, and operational efficiency.
- Key Findings:
- The device was evaluated by 40 experts and professors, showing a high level of acceptability in terms of design and performance.
- The study found that as the gauge thickness of steel increased, the tacking time also increased, while power consumption rose correspondingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a portable arc welder and how does it differ from traditional welders?
A: T a portable arc welder has this distinct advantage of being lightweight and compact, which makes it easy to carry around for use in multiple locations. Like all other welding tools, its output is uncompromised, so it can be used for onsite repairs or outdoor projects. Unlike portable arc welders, traditional welders remain fixed in one place.
Q: How does MIG welding differ from MMA welding in portable applications?
A: In MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, a wire electrode is fed through a welding gun into the weld pool, which makes it very suitable for intricate and detailed tasks. MMA, or Manual Metal Arc welding, is done with a coated electrode consisting of consumable flux. In portable tasks, MIG welding ensures tidier welds while MMA welds are easier and more adaptable.
Q: What safety measures should be considered when using a welding helmet during portable welding?
A: As for the helmet, it should always be done in order to block dangerous ultraviolet rays, sparks of fire and any welding radiation directed to one’s welding face and eyes. Also mind the weigh of the helmet. Furthermore make sure the helmet is well-balanced in weight while containing adequate ventilation filters to attach with goggles.
Q: Are portable arc welders suitable for fabrication services?
A: Due to their versatility, portable arc welders can be used for fabrication and weld processes. They ensure the quality of welds needed for fabrication of parts and structures in different locations.
Q: What makes an engine-driven welder favorable for welding outdoors?
A: Since there is no electricity available in remote locations, engine-driven welders serve as a reliable power source. They provide a variety of portable welding services and ensure quality welding results regardless of the location.
Q: In what ways do built-in characteristics of portable welders improve their use?
A: Functionality can be enhanced with built-in features like adjustable welding output, overload protection, and easy-to-read displays. These elements allow for safe operations and increases control precision while welding.
Q: How important is precision in portable arc welding?
A: Precision is key for portable arc welding because it tightly controls strong and clean welds. There are standards that must be achieved and they need the appropriate strategies for achieving it.
Q: What advantages does a small size offer to portable welding equipment?
A: Small size advantageously provides easier transportation and maneuverability of welding tools in compact places. Alongside this, small size makes storage easy which allows set up in different locations and improves usability in many places.
Q: Is there a distinct class of materials best for Portable Welding Applications?
A: A wide variety of materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminium fall under portable welding applications. The material selection highly depends on the welding procedures done upon (MIG or MMA) and how the end product will be used.

