Picking the right cutting tool is critical for project completion, especially when it comes to precision work. You can select from laser cutters or CNC machines, both of which are powerful tools and have distinguishing strengths and applications. This article distinguishes between the two technologies; how they operate, their uses, and what aspects to keep in mind. You will end up knowing the best insight for making your decision which tool is best suitable for you after reading this.
What Exactly Is a Laser Cutter and How Does It Relate to CNC?

Laser cutters are machines that cut, engrave, or etch materials with extreme precision by utilizing a focused beam of light. Since they are computer operated, intricate designs can easily be programmed into them. CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, is where the operation of laser cutters, routers, and mills is done automatically through a computer. A laser cutter is a CNC machine that is made solely to cut and engrave using lasers. Both need the precise input of a computer to achieve accuracy.
Primary Laser Cutting and Engraving Performance Influences
Laser cutting and engraving can be done efficiently because of the type of material, laser power along with the speed. Choosing the right material is very important especially if it is wood, acrylic, metal, or fabric as each responds differently to the laser’s heat and intensity. For example, softer materials such as wood are easier to cut than metals such as stainless steel which need more power.
Improvements in laser technologies has enhanced the speed and accuracy of laser cutters. Engraving is now possible at speeds greater than 1000 mm/sec, although this depends on material and machine parameters. Furthermore, thinner materials are less time consuming to cut whereas thick materials have to undergo multiple passes or need slower speeds to be cut efficiently.
Business reports claim CO2 lasers are used widely for non metallic materials while fiber lasers have a better performance for cutting metals because of their efficiency with energy and shorter wavelengths. As an example, fiber lasers demonstrate their usefulness on industrial applications by performing up to 20 meters per minute when cutting thin steel sheets.
Orthogonal machine settings, including speed, focus and frequency, with the nature of the materials enable modern laser cutters to work with remarkable precision and efficiency. These innovations underscore that the right selection of tools and settings greatly enhances productivity and quality.
The Impact of Laser Power on Cutting Precision
Power is vital in determining the quality of work done in a laser cutting operation. Increased laser power has a direct relation with material penetration; greater power results in more effective and thorough cuts on thicker materials due to the deep penetration achieved. For example, while cutting mild steel, a 2000 watt laser power would be enough for 6mm thick sheets, but for those above 12mm, the power would need to exceed 4000 watts.
On the other side, too much power can result in emerging problems associated with material overheating. This causes burn marks, deformation, and loss of structural integrity and strength within the material. These issues can be adjusted by balancing power levels based on material type and thickness. Using lower-powered settings with dynamic adjustment methods enhances precision for more delicate items such as thin sheets of aluminum or complex shapes within acrylic sheets.
Moreover, contemporary laser cutting machines use dynamic power adjustments in tandem with advanced sensors and other forms of feedback mechanisms. This allows for real time control of the laser’s performance as it cuts, balancing cutting speed with material conservation. Energy consumption also matters significantly because optimizing power usage increases cost savings while fostering eco-friendliness in a sustainable industrial setting. Adapting these technologies enables manufacturers to achieve uniformity in production while reducing waste and costs.
The Integration of CNC Technology in Laser Cutting
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems have greatly improved the adaptability and accuracy of laser cutting machines. With the inclusion of a Computer Numerical Control System, manufacturers can achieve automation and control over operations like never before. It is now possible to accurately implement complex patterns where the laser scans pre-programmed trajectories down to the micron level.
Modern laser cutters with CNC systems have other capabilities such as real-time supervision and participative regulation of cutting parameters. These advancements help streamline material cutting processes, leading to reduced waste and increased efficiency. Recent reports from industry studies show that integrating CNC systems can boost cutting speed by as much as 30 percent while drastically lowering the rates of mistakes, translating to greater savings in the long run.
In addition, CNC systems ease integration with numerous file types like CAD and CAM, broadening the scope of design possibility. This is especially useful for automotive, aerospace, and electronic industries where extreme accuracy and customizability is critical.
In the fields of laser cutting, merging it with CNC technology will allow manufacturers us to optimize their equipment, fostering innovation and keeping pace with ever-growing market demands.
What Are the Key Differences Between CNC Machines and Laser Cutters?
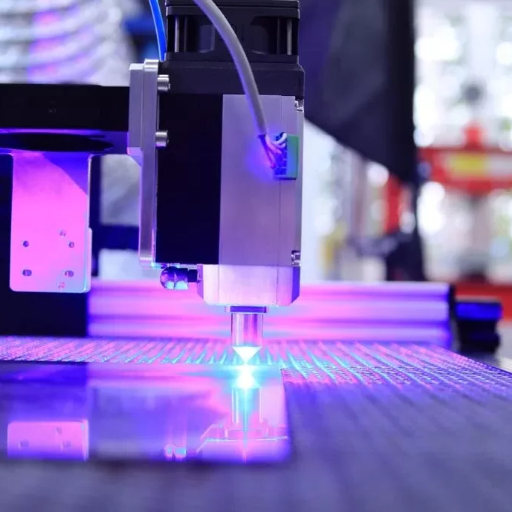
- In the case of Material Removal vs. Heat Cutting, CNC machines remove material using tools such as drills, mills or lathes, whereas laser cutters perform cutting and engraving by melting or vaporizing the material using concentrated beams of lasers.
- With regard to Material Compatibility, some materials CNC machines can work on include metals, plastics, and wood. In comparison, laser cutters are mainly suited for thin acrylic, paper and light metals.
- When it comes to Precision and Detail, CNC machines are better at making parts that need to be strong and rigid. on the other hand, laser cutters tend to be better for more detailed and intricate cuts as such designs need greater precision.
- In terms of Applications, CNC machines are more common for manufacturing processes, which include milling, turning, or drilling. Engraving and cutting complex patterns is done best with laser cutters.
Cutting Performance and Efficiency
Laser technology boldly eclipses traditional tools in cutting precision and speed. Modern laser cutters, especially with the development of CO2 and fiber lasers, are capable of achieving cutting accuracies within microns, making them preferable in industries which need delicate work done like jewelry or intricate electronics. Moreover, new data suggests that high-powered fiber lasers can cut metals, such as stainless steel, into pieces as thin as 50 inches per minute, which is many times faster than what traditional tools can muster due to reliance on manual operation and wear-and-tear.
Another advantage of laser cutting is the efficiency with which materials are used. The precision of the cut laser beam means lower kerf (cut width), therefore, waste is minimized. For example, studies estimate that at least 30% of material compared to traditional tool cutting is not used – highlighting the economically and ecologically friendly benefits of laser cutting.
In addition, automation in laser cutting systems decreases the amount of manpower as well as operational costs. The presence of features such as CNC integration enables precision and repeatability to be automated, improving productivity for bulk manufacturing. On the other hand, laser cutters often come with substantial upfront expenditures along with ongoing maintenance requirements, something that could be detrimental to smaller firms. At the same time, more traditional cutting implements, while less precise and slower, are simpler and more affordable for uncomplicated tasks or one-off jobs.
Materials Processing Capabilities of Both Technologies
When it comes to the processing of materials, laser and traditional cutting methods have different capabilities designed for distinct uses and materials. Processes apart from the basics, laser cutters outperform for many other means considering the vast array of materials they can cut like; metals, plastics, wood, glass, and even composites. For example, modern fiber lasers can cut stainless steel and aluminum with thicknesses of 1 inch or more, depending on the wattage and machine configuration.
The ability of laser cutters to achieve complex designs while minimizing waste is one of their critical advantages. The cut accuracy of laser beams can be as fine as ±0.002 inches which makes laser cutting ideal for the aerospace and electronics industries. Additionally, laser cutting accomplishes productivity greater than mechanical tools by operating at speeds over 1,000 inches per minute on thinner sheets.
Simple tasks such as linear cuts on thick materials are better suited for traditional cutters like mechanical shears and saws. Although they do not possess the ability to perform complex geometries, these tools are the ideal choice when price and basic functionality take precedence. Heavy pipes and beams, for instance, can be cut using circular saws, though these will need additional finishing compared to the edges produced by lasers.
Another aspect to consider is the sensitivity of the material to heat. Laser cutters have the distinct advantage of localized heat input, but even they may experience a secondary effect known as heat-affected zone (HAZ) which changes the heat properties of certain materials, although assist gases such as nitrogen and oxygen help some. Industrial processes have lower thermal input but will often create mechanical work on the part that will, in some instances, produce thermal damage as well.
In any case, the most important factors to make a decision on which technology to implement are specific requirements of the project, material to be processed, and the budget available, all bearing additional methods of cutting which fulfill particular industrial demands.
Comparison Between Precision, Accuracy, and Cutting Speeds
In my opinion from the field, the cutting method determine precision and accuracy differently. Lasers have the range of precision cutting to the point of detailed engravings due to the small size of the beam and amount of power used. On the other end of the precision spectrum, traditional cutting offers desk top level precision with almost no detail. In terms of cutting speeds, laser cutting outshines the competition with thin and well-defined materials or pieces and complex shapes. Personally, I would prefer one over the other depending on the most important task or goals of the project.
What Types of CNC Machines Include Laser Cutting Capabilities?

CNC machines that have laser cutting capabilities are essentially high precision cutting machines. A high powered laser beam is employed to cut and engrave the desired material. The commonly used forms are CO2 laser cutters, fiber laser cutters and diode laser cutters. Their applications span from manufacturing and automotive industries to sign making due to the precision and speed they offer.
CO2 Laser Cutters as CNC Systems
CO2 laser cutters rank among the most popular laser cutting systems on account of their adaptation and accuracy. These machines operate by using a focused beam of infrared light to cut through or engrave acrylic, wood, leather and some plastics. The power output of these lasers is anywhere between 30 watts to several hundred watts, making them ideal for both small businesses and industrial settings.
According to the most recent information, CO2 laser cutters can achieve speeds of several hundred millimeters per second, quantified with a rasters per minute (RPM) metric. For example, a CO2 laser cutter with a 150 watt power rating is able to cut through 6 mm thick acrylic sheets at an approximate speed of 20–30 mm/s. These systems are also capable of supporting busier functions such as automated material handling, sophisticated software, and real-time tracking which can all together ameliorate productivity and reduce downtime.
Moreover, CO2 lasers are extremely popular because one of their main features is the speed at which they create smooth edges of great accuracy, which minimizes the amount of work needed afterward. This is important for verticals like signage and product design. Advancements in the technology have also been able to improve the life span and energy efficiency of the lasers, ensuring lower CO2 operational costs and extending machine usage without needing frequent replacements.
Fiber Laser Cutting Machines and Their CNC Components
When it comes to material processing, the greatest increase in productivity comes from Fiber laser cutting machines which have improved precision, speed, and versitility. These laser cutting machines are best suited for metal and other hard materials due to their delivery of high-powered laser beams which makes use of fiber optics. The performance of fiber laser machines is greatly enhanced by CNC (Computer Numerical Control) parts which manage the cutting order and parameters during operations.
Today, the technology dealing with fiber lasers is modernly advanced and they are now boasting ever greater power outputs with machines for instance offering laser power from 1kW up to 20kW based on the needed application. As an example, when cutting thin steel sheets, a 6kW fiber laser effortlessly performs the cutting at 20 meters per minute which quater times production time when compared to traditional practices. Not to mention, fiber lasers also outperform other lasers in regard of beam quality when it comes to smaller focal diameters leading to better cutting accuracy and intricate designs to be produced with lesser material waste.
The laser machines have advanced quite significantly in recent years as compared to the older CO2 systems. One of the key areas of advancement is energy efficiency. A Fiber laser’s productivity, according to recent research, is greater than 40 percent while the older CO2 counterparts lag behind 20 percent. This leads to a major reduction incost, while also being beneficial to the environment.
Moreover, the real-time monitoring and adaptive systems help with controlling errors with the CNC components, leading to reduced human mistakes and enhanced quality in the items being mass produced. The aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing sectors heavily depend on these equipment. The multifunctional systems have proven to be capable of cutting and welding along with engraving and drilling at impressive precision and speed.
The demand for green methods of production alongside efficiency is on the rise, which is why the fiber laser machines are evolving at a quicker pace as compared to the advancements with CNC technology.
A Thorough Comparison of CNC Laser Cutting, Routers, and Milling Machines
In almost any manufacturing activity, CNC laser cutting, routers, and milling machines have different purposes based on the processes they serve. To add, each of them has its own set of functionalities to meet varying production requirements. Materials like metals, plastics, and wood can be cut or engraved with extreme precision by CNC laser cutting as it focuses highly powerful laser beams on them. It also does an amazing job with intricate designs. On the other hand, CNC routers and milling machines perform physical cutting (as opposed to the fairly rudimentary process of laser carving), which works best with thicker or denser materiales, such as aluminum or hardwood.
Speed and accuracy stand as one of the distinguishing factors CNC routers and milling machines have over laser cutting. Thin metal sheets are rude yet polished at mind boggling speeds of up to 40 m/min. And advanced fiber laser technologies are now capable to enhance referencia posicional de corte up to ±0.03 mm, which works well for some industries, but others that need minute details better restrain their focus on less intricate pieces.
These technologies differ from each other regarding energy efficiency and maintenance costs. Fiber laser machines have significantly lower power consumption than traditional routers or milling machines. For example, some advanced lasers consume wastefully only 30% of electrical power relative to the optical output produced as waste. By contrast, routers and mills have bigger, more mechanical setups that require greater, ongoing, upkeep expenditures due to wear-and-tear of the cutting tools.
There is also greater material versatility. Lasers cut highly reflective materials like stainless steel and brass, while routers are better suited for three-dimensional sculpting and deep cuts into rigid materials. Milling machines, meanwhile, dominate machining metals such as titanium or high carbon steel.
As always, deciding on one of these machines comes down to the specific project at hand: the desired level of precision, the materials, and the costs involved.
What Materials Can Be Processed with Laser Cutters vs. Other CNC Machines?

Laser cutters efficiently process non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and plastic, as well as thin metal sheets. Other CNC machines like routers and milling machines are more effective when cutting hard and tough materials like hardwood, aluminum, brass, and steel. The choice of machine and its effectiveness depend on the material’s thickness, hardness, and the precision required.
Metal Cutting Capabilities Continued: Efficiency and Precision
Cutting accuracy and efficiency are defined by the power of the laser, the material’s type, thickness, and focal length. With the more recent development of laser machines, automated technologies that adjust settings for the most efficient results have been integrated. These advanced features ensure optimal performance, increasing accuracy and production speed.
As an example, 10 mm acrylic works best with 100W CO2 lasers for faster edge processing. In contrast, 2 mm plywood performs best with lower-framed lasers (40W-60W) that offer accurate, char-free cuts.Moreover, advanced cooling systems and air-assist capabilities have improved laser cutters by helping to dissipate heat and clear away debris during cutting. As a result, equipment maintenance is less frequent due to cleaner cuts and decreased wear over time. Many modern laser cutters come provided with integrated software which allows for detailed customization of designs and control over speed, further enhancing production efficiency.
New developments in diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) lasers also provide astonishingly accurate engraving and cutting of detailed designs on metal and ceramics, illustrating how diverse laser technology is in modern society.
Metal Cutting Technologies Continued: Industrial Effectiveness and Accuracy
Like other technologies for metal cutting, CNC milling and fiber laser cutting have particular strengths to meet distinct industrial demands. CNC milling remains a popular choice for processes that require high durability and versatility across different materials. It performs exceptionally well in large-scale production involving intricate geometric shapes because of consistent repeatability and exceptional complex geometry capabilities. However, Cuting fiber lasers set themselves apart with astounding accuracy and speed when working with thin to medium-thickness metal sheets. Fiber lasers achieve smooth edges and intricate designs with astounding efficiency and minimal material waste by applying light to the workpiece.
Recent information indicates that fiber laser cutting systems can operate at astonishing speeds, enabling them to fully cut through materials like stainless steel with 20mm thickness at 6kW level with ease. Additionally, the speed of cutting for thinner metals is around 60 meters per minute, making production significantly faster than traditional methods. Further increases to the efficacy of fiber laser systems is attributed to the automated nozzle changers, real-time cutting optimization software, and adaptive beam shaping technology these systems incorporate. These also add to the flexibility and superb, timeless precision required in automation, aerospace, automotive, and electric laser industries.
Different Available Technologies For Materials And Their Boundaries
In the realm of fiber laser systems, effectiveness stretches far past just simple cutting and engraving. Not only is it renowned for precision but the versatility in engraving is unmatched. These systems efficiently cut through metals like stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass due to their high absorption rates for laser wavelengths. There are non-metal materials too, such as plastics, ceramics, and a few composites that can be processed. However, the efficiency and quality of those materials is heavily dependent on their composition and thickness.
The effectiveness of CO2 lasers is cutting non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, glass, and leather. The type of metals they can cut are limited to those that have thinner layers of coatings or preparations due to the metallic surfaces having lower absorption efficiency. The application of both fiber and CO2 lasers may be further restricted by the reflective properties of some of the materials, which would require precise settings to mitigate damage or inefficiencies.
It is noted in the data that fiber lasers are more efficient for energy saving purposes by converting 70% of electrical input to laser light while CO2 lasers only operate at 10 to 20 percent efficiency. CO2 lasers have shorter operational lifetimes; approximately 30,000 compared to 100,000 hours with fiber lasers. Alongside these advantages, fiber lasers are limited to their reduced ability to cut thicker non-metallics, while CO2 lasers more economically useful for larger non-metal surface machining.
Both ways provide advanced powerful solutions for problems at hand, but focus needs to be improved in balance with the strengths and limitations the methods have. Blend the type of laser for tailored materials to optimize performance, efficiency, and cost across industrial applications.
How Do I Choose Between a CNC Machine and a Laser Cutter for My Project?

- Material Type: The harder materials like metals and wood are best cut and shaped using CNC machines. For thinner, non-metallic materials like acrylic, fabric, or paper, laser cutters are best suited.
- Precision Needs: CNC machines are best used for projects that are centered around heavy shaping and engraving as they are accurate, but less detailed compared to laser cutters.
- Project Scale and Budget: For larger scale and more heavy duty projects, CNC machines are more flexible and efficient, though their operation comes at a higher cost. As for smaller pieces, laser cutters are more precise at a lower cost.
Marking Speed and Cutting Efficiency Factors
Many factors must be considered when choosing the ideal cutting method if the goal is to ensuring fast and efficient work. One of the most important points to consider is the cutting effect and material properties. For example, metals such as stainless steel or aluminum would need high amounts of energy to cut, while acrylic or wood can be cut with ease at lower energy levels.
Furthermore, the machine settings and the tools set together dictate the cutting parameters like the speed and the depth . More precise tools, like laser cutters, can perform the intricate designs at very high speeds. For example, some advanced CO2 laser cutters are reported to operate at between 10 mm/s to over 300 mm/s depending on the material and its thickness. CNC routers, on the other hand, are much slower but perform deeper cuts while maintaining robust structural integrity of the part.
Also important is the cutting efficiency and cost associated with carrying out the operation. The initial purchase price of laser cutters may seem excessively high compared to other cutting tools, but their lower maintenance costs and increased speed often outweighs the initial cost in the long run. On the other hand, CNC machines are regarded as reliable machines, laser CNCs have higher running costs due to slower processing times and constantly needing maintenance and tool changes.
Here the combination of material properties, operational costs, and speed requiements allows managers to decide between laser cutters and CNC machines while ensuring the projects keep precision and cost effectiveness in balance.
Cost Efficiency and Performance Factors in CNC Technologies
In the case of CNC technologies, several parameters impact the balance between cost efficiency and performance. Industry feedback suggests that new high speed CNC machines are capable of reducing the cycle times of a process by as much as 40%, which is extremely beneficial for productivity in volume manufacturing. The investment for advanced systems is also very high, from $50,000 to over $500,000, depending on the model and features of the machine.
The type and usage of the machine also affects maintenance costs greatly. Take, for example, machines equipped with linear motors. They are generally more accurate and have a much lower long term maintenance cost. In contrast, the more traditional ball-screw systems require lubricating and periodic adjusting. Other operators should take note of the energy CNC machines consume because modern equipment can lead to 20% lower cost in operational expenditure annually compared to older systems. Those equipped with energy efficient components are even more cost effective.
Tooling cost is another factor that needs to be managed effectively considering the type of materials as it relates to wear and tear rates as well as replacement intervals. For example, cutters made from carbide are still prefered for more challenging materials such as titanium and stainless steel, as they are less expensive, but only up to 10-20% per unit compared to high speed steel. Firms that balance tool selection with machining parameters will achieve a high level of cost efficiency relative to production and many associated factors.By balancing these factors of cost and performance, businesses can rationalize the return on investment for their CNC technology in terms of capital spent and production goals achieved.
When to Use CNC Laser Cutting vs. Other CNC Processes
Both CNC laser cutting and traditional CNC processes have different pros and cons depending on the application, material and level of precision. CNC laser cutting is most efficient when dealing with intricate designs because lasers cut with a very small kerf on the material which leads to more accurate and detailed results. The numbers speak for themselves: laser cutting machines can achieve tolerances of up within 0.003 inches, and that is beneficial for the electronics, aerospace, and even jewelry industries, which are precision-focused.
Turned and milled CNC are more traditional processes for thicker materials and other projects that need heavy duty tools. For example, the CNC milling of steel and titanium parts is common since these materials are more difficult to machine and require considerable mechanical strength. It has been observed that traditional CNC machines are more cost effective when dealing with high volume production runs due to quicker cycle times and greater tool assortment.
CNC laser cutting is typically faster than traditional methods when dealing with thin materials, although it is more costly per unit. Most fiber laser cutters outperform most mechanical cutting methods with speeds up to 100 inches per second. In time-bound industrial production settings, the difference in speed is critical.
With regard to cost, precision, and material properties, business objectives dictate which method is employed. Companies focused on precision and speed regarding thin materials will favor CNC laser cutting. Those focused on durability and cost efficiency for larger, bulkier projects will utilize traditional CNC.
Reference sources
1.Study: An Overview Study on Laser Technology and Applications in the Mechanical and Machine Manufacturing Industry1
- Objective: To explore the applications of laser technology in mechanical and machine manufacturing, with a focus on laser cutting and its integration with CNC systems.
- Methodology: The study reviewed the principles of laser operation, its technological advancements, and its applications in various industries, particularly in material processing and manufacturing.
- Key Findings:
- Laser cutting machines are often integrated with CNC systems to achieve precise, high-speed cutting of metals and other materials.
- The CNC system controls the movement of the laser beam or the material, enabling multi-dimensional cutting and engraving.
- Laser cutting offers advantages such as smooth cutting surfaces, high accuracy, and the ability to process complex shapes, making it a preferred choice in modern manufacturing.
- The study highlights the role of laser technology in Industry 4.0, emphasizing its efficiency and adaptability in automated manufacturing processes.
2.Top Hobby CNC Router Manufacturer And Supplier In China
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between a CNC machine and a laser cutter?
A: It is true that a laser cutter falls under the category of a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine. However, there is more to the story. CNC as a concept encompasses a wide range of tools which include a computer-based mechanism that automates the cutting and shaping of different materials. A laser cutter uses a laser beam to cut materials while other CNC machines, for e.g. milling, use blades. The difference lies in the process used. Laser cutters use light energy while older CNC machines remove material using physical bits or tools.
Q: How do CNC cutting and laser cutting compare in terms of precision?
A: Compared to other CNC cutting processes, laser cutting is more accurate. Modern laser cutting tools can reveal very fine features with kerf widths of 0.1mm or less greatly surpassing the ability of other cutting methods. Old CNC milling and router machines can achieve good precision, but the size of the cutting bit imposes limits. There is no tool wear with laser cutting, enabling consistent precision throughout a project. Other machines tend to lose precision with every phase of the job.
Q: Is it possible for a CNC cutter to use the same materials as a laser cutter?
A: There is some CNC and laser compatibility, but respective devices work best with different materials. CNC machines can work with a broader list of metals, hardwoods, and plastics and are best at cutting thicker materials. Laser cutters are adaptable, but not with reflective metals and some plastics. The most common of such machines, CO2 laser cutters, work best with organic materials like wood, paper, acrylic, and fabric, though these materials cannot be too reflective or have a high melting point.
Q: Is the cost of CNC cutting equipment the same as laser cutting?
A: The difference of the cost can be very noticeable; yes. The cost to purchase laser cutting equipment is usually much greater, particularly with industrial level machines that have more advanced power laser sources; these enter at about 15-20,000 dollars. Starting level CO2 laser cutters are around 2,000 dollars with professional models within 10,000 to 50,000. Traditional CNC routers or mills commonly cost less upfront, yet, mass produced CNC machines used in manufacturing also have large price tags. Additionally, operating costs differ- cutting lasers need their tubes replaced at intervals, while their CNC counterparts operated with cutting bits that have to be swapped out regularly.
Q: In which circumstances are CNC milling and laser cutting applicable in different ways?
A: The application disparity between CNC milling and laser cutting is attributed to their different capabilities. While CNC milling is capable of operating in 3 axes, making it possible to create complex 3D shapes and engravings, harder materials like metals, and using tools which remove materials, laser cutting works best with intricate detail while producing 2D cuts and engravings. Laser cutting accomplishes precise cuts without damaging materials, while milling is used to add structure to materials with 3D contours and precision.
Q: What benefits does laser cutting have over CNC machining?
A: Laser cutting does have one or two clear advantages over CNC machining. Compared to CNC, laser cutting provides faster production speeds, edge finishing, and ensures cleaner edges. Additionally, less material is wasted in the process, as well as no pressure being applied to the object being cut. This is why laser cutters are better focused on thin materials. Lastly, switching between cutting projects is faster as there is no need to interchange physical tools.
Q: What factors do I need to consider when deciding between a CNC cutter and a laser cutter?
A: Think about the requirements for your particular task when picking between the CNC cutter and the laser cutter. If your work includes cutting thinner materials (less than 1/2 inches) and requires greater detail, or if your work revolves around acrylic, wood, fabric, or paper, then a laser cutter would be ideal. If your work entails working with thicker raw materials and metals, necessitates 3D carving, or deals with structural pieces where material strength is a factor, then a CNC machine is preferable. Some workshops find it beneficial to possess both technologies since they are both useful for different purposes.
Q: Are there machines that incorporate both laser cutting and CNC functions?
A: There are, however, hybrid machines that include both laser cutting alongside CNC milling. These machines usually have interchangeable heads, one of which is a laser module and the other is a mechanical cutting spindle. Such versatility allows for laser cutting when fine precision is needed, while CNC milling can be used for 3D carving or processing thicker materials. These hybrid machines do provide multifunctionality, but they tend to be weaker in specialized power and functionality when compared to dedicated machines. Prototyping shops and small scale manufacturers that do varied operations without space for numerous machines freely use them.
Q: What safety considerations differ between CNC and laser cutting?
A: These technologies differ greatly in their safety considerations. Laser cutting has additional risks peculiar to it, such as the presence of laser radiation, which may damage the skin and eyes and, therefore, requires some operations to be enclosed and filtered. Also, laser cutting may produce fumes that are harmful to health and, dependant on the material being cut, increased ventilation or filtration systems will be required. CNC cutting machines pose mechanical risks of rotating parts and tools, as well as the proprietary danger in the form of debris. All systems require appropriate training, but with laser systems, there is usually more protection needed because of the hazards that are not seen. For both equipment types, recommendations of the manufacturer should be followed.
- How Laser Cleaning Technology Works: Laser Cleaner Basics
- Diode vs. CO2 vs. Fiber Laser: Choosing the Best Laser Engraver for Metal
- Unlocking the Secrets of the 3D Laser Marking Machine: A Comprehensive Guide
- Unlocking the Power: How Does Laser Cleaning Technology Function?
- The Future of CNC Machining: How the CNC Industry is Revolutionizing Manufacturing
- Maximum CNC Router Cutting Thickness: What Thickness Can Your CNC Router Cut Through Wood?
- The Ultimate Guide to Laser Surface Cleaning Safety: Protecting Yourself While Using a Laser Cleaner
- Why CNC Machining is More Popular Than 3D Printing in Modern Manufacturing

