With their unrivaled precision, versatility, and efficiency, CNC routers have transformed the manufacturing industry landscape. For hobbyists and professionals, knowing how to make the most of a CNC router for metalworking can boost projects to new heights. Whether you are a one-man band or a member of a large manufacturing outfit, this guide aims to demystify the use of CNC routers on metal pieces. We will focus on the critical steps from machine selection to the cutting process refinement that will lead to perfect outcomes. With the knowledge shared in this article, you will understand the techniques needed to enhance your efficiency while effortlessly completing excellent, high-quality outputs.
What is a cnc router machine?
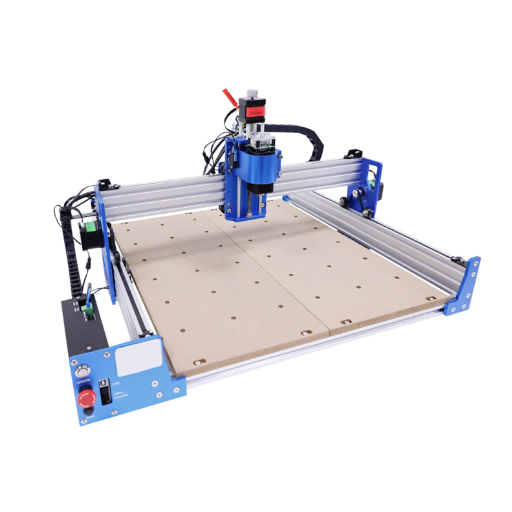

A cnc router machine is a “cutting” tool controlled by a computer and functions as a saw, engraver, or mill, servicing wood, metal, plastic, foam, and other composites. It follows all programmed instructions, which include moving to designated paths to execute intricate designs and precise cuts expertly. It achieves this through the CNC (Computer Numerical Control), which performs writing quickly, accurately, and consistently. This makes the CNC router the best in producing, prototyping, or crafting creative designs.
How does a cnc router machine work?
A CNC router machine works by converting a digital design into a movement. The process starts with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, where the design is created. The Software is later changed into a CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) file that forms a complete toolpath. The controller of the machine scans this toolpath and gives commands to the stepper or servo motors where the router is driven along three or more axes, X (horizontal), Y (vertical), and Z (depth). Other sophisticated machines may also add more axes for advanced designs.
The route CNC machine uses captures material using various methods such as Cutting, carving, and engraving. Other methods that could be included are spinning or milling. For example, the spindle could spin at around 8,000 RPM to 24,000 RPM or even higher, depending on the complexity of the material and the precision needed. Modern machines offer precision as fine as ±0.001 inches or tighter, providing notable details essential in other industries like automotive, aircraft manufacturing, and furniture production.
In addition, CNC routers can work with different materials, each with its distinct settings. For instance, when cutting wood, the feed rate needs to be slower and the spindle speed faster, compared to milling aluminum, where stronger tools and coolant flow are required in order to cool the equipment and prevent overheating. Additionally, more sophisticated CNC machines have automatic vacuum tables that hold the material in place or auto tool changers that enhance efficiency in complicated workflows.
These days, the introduction of cloud-based software and IoT-powered systems enables remote supervision of the equipment, further increasing efficiency. With these technologies working hand-in-hand with robust machining functions, CNC routers have cemented their importance across many industries and for creators all over the globe.
What are the components of a cnc router for metal?
A CNC router for metals comprises various critical parts, which include:
- Machine Frame and Gantry: Both the frame and gantry are cut from heavy-duty steel, aluminum, or other rigid material, as these maintain stability and minimize vibrations when machining the workpiece.
- Spindle: The spindle is integral to the machine as it needs to rotate rapidly while providing sufficient power to cut through the different types of metals. Water or air cooling systems are often integrated within the spindle to prevent overheating.
- Controller Unit: The CNC controller executes commands given from the computer and transforms the drawing into movement, executing the work on the machine. It ensures the cooperation of all components to execute the work accurately.
- Drive Systems: The cutting tools are moved along the X, Y, and Z axes by motors like stepper or servo motors that work with lead, ball, or rack-and-pinion screw systems.
- Vacuum or Clamping System: To perform CNC operations, a workpiece must be held securely at rest, and thus, metal workpieces are held by vacuum tables or clamps. Uninterrupted stability is crucial to accomplishing exact and repeatable work.
- Clamping Systems and Cutting Tools: The machine uses different types of cutting tools, such as drills, engraving bits, and end mills, depending on the thickness and type of metal. Tools are easily interchangeable since they are mounted on tool holders.
- Cooling System: The rotary CNC machine is fitted with a coolant system or air blower to help with temperature management. CNC routers generate a lot of heat when cutting metals, which increases the life of the tools and equipment.
- Software Control: The CAD/CAM design software enables users to either upload pre-made designs or create new ones and provides control over the cutting process by translating machine instructions, take control over the cutting process.
- Shavings and Dust Removal: Although not as essential as wood or plastic, some CNC routers are equipped with systems to control the level of metal shavings to keep the workspace tidy.
CNC routers are essential for metalworking due to the increased precision and efficiency offered by the machines and the features of each component.
What differentiates a cnc router from a milling machine?
CNC routers manage softer materials at a quicker pace and possess larger work areas, unlike CNC mills, which are more precise and work with harder materials. CNC mills are slower, yielding more detailed results.
| Parameter | CNC Router | CNC Mill |
|---|---|---|
|
Speed |
Faster |
Slower |
|
Precision |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Material |
Soft (wood, plastic) |
Hard (metal, titanium) |
|
Work Area |
Larger |
Smaller |
|
Axes |
3-5 |
Up to 12 |
|
Cut Depth |
Shallow |
Deep |
|
Applications |
Prototyping, signs |
Aerospace, medical |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
What are the benefits of using a metal cnc router?

- Precision: CNC routers can cut and engrave metals with high accuracy, achieving consistency across all projects.
- Efficiency: Metal CNC routers improve project completion time, as they can run nonstop.
- Versatility: The machines can work with a wide range of metals and execute multiple functions, such as cutting, engraving, and drilling.
- Cost-Effectiveness: They also reduce the total cost of production by minimizing material waste and lessening the required manual labor.
- Ease of Automation: Metal CNC routers enable better workflow and productivity since, once programmed, they need very little supervision.
How does precision improve metal fabrication?
Accuracy, consistency, and quality, which enhance metal fabrication processes, are made possible through precision. High precision enables metal CNC routers to meet exact specifications during production, reducing errors and material waste. The level of accuracy is critical in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries because even the slightest deviation can compromise performance and safety. Most recently, Google reported a surge in the demand for advanced manufacturing technologies. Their research states precision machining ranks highest among other sectors where manufacturers wish to optimize operations and address complex industry requirements. Precision in metal fabrication also lowers the need for replanning and adjustments after production, improving part fitting and decreasing assembly time, which enhances cost savings and product reliability.
What types of metal can be cut with a cnc router?
Modern CNC routers are exceptionally adaptable and can precisely and efficiently cut soft metals like aluminum, brass, copper, and mild steel. Depending on the machine’s power and tooling, some advanced routers can process tougher metals like stainless steel and titanium. Current Google data suggests that aluminum is the most popular option. This is probably because of the lightweight metal’s ease of use across numerous industries. Appropriate tooling and feed rates are crucial to cut cleanly and accurately, allowing manufacturers to use CNC technology for precision production across various metal types.
Are there advantages to using a cnc router over traditional methods?
Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, CNC routers offer a plethora of benefits. They have become essential in many industries because of their accuracy, effectiveness, and adaptability. The following are five significant advantages of using CNC routers:
- Increased Precision and Accuracy
CNC routers can achieve exceptional levels of precision, often within tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches. Traditional methods that involve manual work are subject to human error, where different pieces might be produced inconsistently. With CNC technology, consistency and repeatability automate processes essential for high-end manufacturing.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
Cutting, drilling, and shaping with CNC routers are completed at a staggering speed compared to other methods. These routers require little maintenance, which allows them to run nonstop, even 24/7. The increase in productivity is beneficial when there is a large-scale manufacturing need.
- Lower Waste and Material Expenses
Optimized material usage and programmed precision ensure CNC routers generate significantly less waste than traditional methods. Erroneous production processes are minimized, which helps conserve expensive materials and enhances the overall cost while promoting sustainability.
- Increased Range of CNC Routers Application
CNC routers can work with different materials such as wood, plastic, metal, foam, and other composites. Additionally, they can perform multi-axis work, complex designs, and intricate cuts that would be very difficult or even impossible to achieve with traditional tools.
CNC routers reduce a significant amount of work and risk for the person operating them. Unlike traditional methods, where the worker is required to be in close contact with dangerous equipment, CNC routers are automated, which allows operators to control them from a safe distance.
Maintaining quality while scaling up or down in volume has always presented challenges for production. It’s easy to see why CNC routers, like the rest of the production industry, have become increasingly popular.
How to choose the best metal cnc machine for your needs?

- Material Compatibility
Confirm that the CNC machine is compatible with the metal you intend to work with, such as aluminum, steel, or titanium.
- Precision and Accuracy
If your projects require tight tolerances, you need to focus on acquiring trusted brands with proven precision and reliability.
- Machine Size
The machine needs to be large enough to accommodate the metal components you will be machining while still being compact enough to fit within your workstation.
- Power and Speed
Consider whether the machine’s power and speed capabilities are adequate for your production requirements for coarse work or intricate detailing.
- Ease of Use
If you are just starting out in CNC machining, look for machines with intuitive controls and helpful support features.
- Budget
Purchase decisions should fit within the predetermined budget, considering the initial investment and ongoing costs like servicing, software, and auxiliary expenses.
- Support and Warranty
Defect-laden machines from established manufacturers that offer comprehensive after-sales customer support, training, warranty, and supportive materials should be prioritized.
These factors define the criteria for choosing a CNC machine tailored to one’s requirements and ensuring effective output in metalworking endeavors.
What features to look for in a cnc machine for metal?
When choosing a CNC machine for metalworking, it’s essential to consider factors affecting its performance, efficiency, and adaptability for your projects. The following are five factors that you should consider:
- Durability and Build Quality
A metal CNC machining system should be housed in a durable and reinforced casing, consisting of a rigid frame constructed of cast iron or steel. This durability reduces internal vibrations during use, promoting greater accuracy in the machine cuts and prolonging operational life. For instance, the high-alloy steel frame can perform heavy-duty tasks and endure sustained strain over time.
- Spindle Power and Speed
Spindle power and speed greatly affect the machine’s cutting and shaping capabilities regarding metal toughness. For example, high-power spindles (5HP or more) running at variable RPMs can work on different types of metals, including aluminum and hardened steel.
- Precision and Accuracy
A CNC Machine should be capable of intricate design workflows with tight tolerances. Ensure the machine features high-precision ball screws and linear guides to achieve accuracy, often down to 0.001 inches. Further, advanced motion control software improves positioning repeatability and precision, which is essential for delicate tasks.
- Tooling and Compatibility
The adaptability of cutting tools is paramount for extensive machining. Automated tool changers (ATCs) in the machines boost productivity owing to effortless tool switching. Standard or specialized tool set compatibility broadens functionality while reducing operating expenses.
- Control System and Software
The control system that controls a CNC machine depends on its precision. Intuitive menus simplify operations, while CAD/CAM integration enhances design flexibility. Advanced controllers and simulators provide error minimization and efficiency enhancement, thus optimizing operational performance.
Choosing a machine with these features ensures that your technical and operational requirements in metalworking are met.
How to determine the right size for a cnc router?
Selecting a CNC router’s appropriate dimensions influences its effectiveness for your project. The router’s dimensions affect its overall capabilities and how well it can adapt to your workspace and material needs. Consider the following most important factors when determining the optimum size:
- Workspace Dimensions
As with any equipment, identify the most convenient location to install the CNC router. This entails not only the machine’s footprint but also the clearance required for moving parts and the operator. For instance, in small workshops, benchtop CNC routers of 24″x 24″ or smaller are more appropriate than full-sized industrial models.
- Material Dimensions
CNC routers come in various sizes, from compact hobbyist models with work areas smaller than 12″x 12″ to large industrial machines like 4’x8′ routers used for woodworking and sign making. If a user plans to regularly work on full-size plywood or MDF sheets, then a 4’x8′ router is ideal; otherwise, a mid-size machine would suffice.
- Production Volume
High-volume production usually entails having a greater router capable of managing bigger materials or multiple sheets simultaneously. For example, companies that use 5’x10′ or 4’x8′ CNC routers realize the efficiency of batch production. If you are doing small-scale tasks or prototyping, you can work with smaller ones.
- Z-Axis Travel and Depth of Cutting
The Z axis (vertical axis) travel defines the height of the material that can be worked on. Intricate 3D projects and tasks like mold-making, which involve deeper cuts, demand thick carving and adequate Z axis clearance, so make sure the CNC router provides sufficient Z-axis room. It is common for routers to have a Z-axis range of 6″-8″, but some high-end models can go beyond 12”.
- Standards and usage in the industry
Study trends in your particular industry. For instance, most carpenters prefer 4’x8′ models, whereas smaller desktop machines are more common for jewelry and engraver applications. According to Google Search data, CNC routers with dimensions ranging from 2’x3′ to 4’x8′ were the most searched sizes in 2023, showcasing their practicality and widespread usage.
- Flexibility In Budgeting And Long Term
Typically, larger CNC routers are more expensive. A larger CNC router that fits your current and potential future needs is more economical in the long run. Plan with scalability in mind so you do not outgrow a small machine too quickly.
Considering these factors, you can select a CNC router size that fits your production volume, material type, and available space. The right decision improves operational effectiveness, minimizes waste, and increases satisfaction in your CNC processes.
What is the price range for a cnc router for sale?
The most basic CNC router can be bought for 2500, while high-end industrial models can cost 200,000 and above.
| Category | Price Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Entry-Level |
$2,500 – $5,000 |
For hobbyists, small projects |
|
Mid-Range |
$20,000 – $75,000 |
Advanced features, larger projects |
|
High-End |
$75,000 – $200,000+ |
Industrial-grade, high precision |
How to set up and operate a cnc router for metal?
Make sure that the environment is clean and organized to prevent clutter.
Guarantee that the appropriate CNC router is equipped to deal with metal materials.
Choose and fasten the proper cutting tool. Choose spindle tools that are specifically geared for metal cutting.
- Material Requirements
Position the metallic workpiece accurately and fasten it to the machine bed with clamps or a vacuum table to prevent movement during machining.
Confirm that the workpiece material is aligned with the machine’s capability.
- Calibrating The Machine
Define the starting point of the cut by setting the machine’s zero point (home position).
Define calibrated tool offsets to not be greater than the cutting depth controlled by the height adjustment.
- Software Steps
Add the design to the CNC software.
Lower the feed rate, depth of cut, and spindle rotation to suit the specific type of metal at hand. Consult the machine’s manual for verification.
- Execution
Make a dry run with no cutting implemented to verify the assembly.
After confirming everything is correct, proceed with cutting and watch the machine closely for any signs of abnormalities.
Remain vigilant for problems while wearing eye protection like goggles and gloves.
- After Everything Else
Carefully detach the workpiece from the machine after powering it off.
Check the component for correct dimensions and the quality of the finishing.
Remove all dirt from the machine to prevent failure and ensure it functions seamlessly.
Tools CNC routers for metals demand care, and the steps above will facilitate that for safety and productivity. Like all machines, yours most probably comes with a specific manual, and it’s important to look it up.
What are the initial setup steps for a cnc router machine?
CNC router machines require specific configurations for the setup to ensure safety and accuracy. Follow the steps below for the initial preparation:
- Select the Correct Work Area
Position the CNC router on a flat and sturdy worktable to reduce vibrations and ensure accuracy. Check that the space is tidy and well ventilated to ensure workplace safety.
- Confirm Power Connections
Make sure the power constraints are compatible with the CNC router machine. Connect the CNC router to a stable power outlet, using surge protection.
- Fasten the Required Material
Pick the material to be carved or cut, and firmly place it on the working bed. During operations, the material should not be able to move, thus loose clamping is not accepted.
- Attach Applicable Tool Bits
The tool and the operation required should guide you in selecting the cutting tool (bit). To prevent errors, ensure the tool is fastened securely to the spindle.
- Set the Parameter of the Machine
Material and tool selection will guide setting parameters like the spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut, entered into the software.
- Home the Machine
Accurate operations require the equipment to be hobbled to rest. Thus, CNC routers need all their axes reset to the origin (starting positions) before initializing.
- Assessing System Safety
Conduct a safety dry run, or system simulation, zeichenschnitt, while the cutting tool is not engaged, to assess the software and mechanical systems. Fix any problems that you encounter.
- Open the Worksheet
Before importing the design or G-code file into the CNC machine’s controller, you must ensure that it is compatible with the software.
- Check all components of the system operator protective devices.
As initial steps in optimizing operator safety performance, ensure that the setup of your CNC router machine follows the machine’s manual, where setup details tailored to the model are indicated step by step.
How to program a cnc router for metal cutting?
Precision, safety, and efficiency are paramount when programming a CNC router for metal cutting. To begin, follow the simple steps below:
- Design Creation through CAD Software
First, design the component you wish to cut using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. For example, Autodesk Fusion 360 or SolidWorks allow for the creation of detailed two- and three-dimensional models.
- Translating the Design into G-code
To generate G-code, the CNC machine’s language, use the CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software together with your design. Remember to calibrate parameters like feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut, paying particular attention to the kind of metal at hand.
- Appropriate tools and respective Cutting Parameters
Selected tools should include cutting parts for metalworking, such as carbide and high-speed steel end mills. Set the cutting speed, feed rate, and toolpath according to the metal in use, be it Aluminum or Steel. Check what parameters are best recommended for achieving the desired results.
- Program Transfer to CNC Router
Use a USB or Ethernet to transfer the generated G code to the machine. Check that no errors have occurred in program loading.
- Arrange and Fasten Material
Attach the sheet metal or block to the worktable using clamps or employ a vacuum hold-down system. Proper material positioning is essential to avoid shifting during the cutting process.
- Perform a Scratch Pass
Execution of a ‘scratch’ pass without the use of cutting tools is required to validate the machine program, toolpath, and settings of all components. This avoids material and machine-damaging mistakes.
- Proceed With the Initial Steps of Cutting Metal
With all settings checked and marked verified, commence with machine operation while paying close attention to process flow for any abnormalities. Be ready to stop if the processes exceed normal boundary expectations.
- Machine Part Polish and General Cleanup
Observe the material sample for tailored results before detaching from systems. If necessary, implement any desired endpoint finishing, such as polishing or deburring.
The combination of all these tips alongside your CNC tailored manual will increase accuracy for metal cut programming. Keeping up with advances in CNC software and cutting tools will improve precision, productivity, and turnout.
What safety measures should be taken when operating a cnc machine?
The use of a CNC machine should be violence-free by following safety steps, as the well-being of an operator is of the utmost importance. First and foremost, put on relevant personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles, ear masks, gloves, and steel-toed boots, which help protect him/her from flying debris, voices, and pulleys. Confirm that any loose-fitting attire, jewelry, and long hair are tied up to avoid getting intertwined with moving components of the machine.
Protection practices must be followed for every step of the CNC machine process. Make the necessary preparations by methodically scanning the machine for potential dangers. Measures include: any loose parts, signs of wear and tear, or other hazards. In addition, employing the manufacturer’s instructions and training will keep all procedures in line with any proprietary guidelines. Refrain from using supplemental tools that do not align with the machine’s specifications. Guard fences and case protectors ought to be used as they constitute an unduly barrier against exposure to moving parts of the machine.
The workspace should be kept organized, free of unnecessary clutter, and maintained to mitigate the chance of someone tripping or interfering with machine operations. All operators should be trained and familiar with emergency shut-off procedures, detailing how to turn off the machine swiftly in case of a malfunction. Regular maintenance check-ups must be scheduled to improve the machine’s performance and reduce mechanical failure. Furthermore, operational safety can be enhanced by staying informed on the latest industry safety standards and advancements in CNC technology.
Under no circumstances should a CNC machine be left unattended during operation, and equipment should not be used while fatigued or distracted to guarantee undivided attention to the task. Observing these practices enables CNC operators to enhance workplace safety while increasing efficiency.
Reference Sources
- “4 Axis Mini CNC Router for Metal Round Materials” (Sales et al., 2001, pp. 227–240). This paper, published in 2001, describes a 4-axis mini CNC router designed for machining metal round materials. While older than your 5-year timeframe, it’s relevant to the topic. The methodology and key findings are not detailed in the provided abstract.
- “U Shield 3 Axis CNC Router Training in Tegal City Metal Group to Improve Machinery Capability” (Santoso et al., 2022.) This 2022 paper discusses training on a U Shield 3-axis CNC router within a metalworking group. The focus is on training and skill improvement, not the specifics of metal machining with the router. The methodology involved a soft and hard program approach to training. The key finding was that participants improved their understanding and practical skills in using the CNC router.
- “CONSTRUCCIÓN E IMPLEMENTACIÓN DE UN PROTOTIPO DE ROUTER O FRESADORA MEDIANTE CONTROL NUMÉRICO COMPUTARIZADO (CNC) CON SOPORTE EN MACH3” (Pérez et al., 2016). This 2016 paper details the construction and implementation of a CNC router prototype. While the material isn’t specified, using MACH3 software suggestsa potential application to metal, though this is not explicitly stated. The methodology involved building and testing a prototype with basic geometries on MDF and acrylic. The key finding was successful prototype construction and operation.
- Top CNC Router Manufacturer and Supplier in China
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a CNC router for metal?
A: A CNC router for metal is a computer-controlled cutting machine designed to carve, engrave, and mill various types of metal, including soft metal materials. It utilizes high precision and different cutting tools to achieve intricate designs and shapes.
Q: Can a CNC router engrave metal?
A: Yes, a CNC router can engrave metal using specialized engraving machines or tools. Metal engraving can be done for decorative purposes or to create detailed designs on metal surfaces.
Q: What is the difference between a CNC router and a CNC milling machine?
A: A CNC router is primarily designed for cutting softer materials like wood and plastic, while a CNC milling machine is built for higher precision machining of harder materials, including metal. CNC milling machines often have more robust spindles and can handle more complex operations.
Q: How does a laser cutter compare to a CNC router for metal?
A: A laser cutter uses a focused beam of light to cut through materials, which can be very precise and clean. In contrast, a CNC router uses mechanical cutting tools to carve and engrave metal. Both have their advantages depending on the type of work being done.
Q: What is a mini CNC router, and is it suitable for metal work?
A: A mini CNC router is a compact version of a standard CNC router suitable for smaller projects. While some mini CNC routers can handle soft metal materials, they may not be suitable for more robust metal engraving or milling tasks.
Q: What are the benefits of using a 4×8 CNC router?
A: A 4×8 CNC router offers a large work area, making it ideal for handling bigger projects, including large metal sheets. This size allows for versatility in woodworking and metalworking tasks, enabling users to create larger designs without needing to reposition the material.
Q: What types of metal can be processed with a CNC router?
A: A CNC router can process various types of metal, including aluminum, brass, and other soft metal materials. A CNC milling machine is typically recommended for harder metals due to its higher cutting force and precision.
Q: How do I choose the best CNC router for engraving metal?
A: When selecting the best CNC router for engraving metal, consider factors such as spindle speed, precision, the type of metal you will be working with, and the size of the work area. Additionally, look for models specifically designed for metal engraving or that have compatible tooling options.
Q: Can I use a CNC router for aluminum cutting?
A: Yes, a CNC router can be used for aluminum cutting, particularly if it is specifically designed as a CNC router for aluminum. Using the correct cutting tools and settings is important to ensure the best results.
- CNC Router: Cut Carbon Fiber, Cutting Carbon Fibre on a Machine
- Understanding Bevel vs. Miter Cuts: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Class II Lasers: What You Need to Know on Them From a Safety Point of View
- Understanding the Crucial Differences Between Laser Engraving vs Laser Marking: A Complete Guide

