Those venturing into modern manufacturing and precision engineering need to understand the basics of CNC machines. Providing unrivaled accuracy and automating complex processes, these machines have improved efficiency like no other. Despite their vast importance, the different classifications of CNC machines can seem overwhelming. The aim of this guide is to simplify things— demystifying the five most common types of CNC machines by summarizing what each does and their significance in the industrial landscape. In addition, professionals and newcomers alike will be able to understand the foundational material regarding the capabilities and roles of CNC machines with this article.
What are CNC machines and how do they work?

CNC machines, or Computer Numerical Control machines, are precise manufacturing tools that are fully automated and controlled by a computer. They perform operations such as cutting, drilling, or shaping metals, wood, and plastics based on guided G-code instructions. The level of precision, repetition, consistency and efficiency achieved through these processes unmatched in the history of manufacturing.
The Advancements in CNC technology
It is true that more recent years gave birth to Northam’s adapting artificial intelligence alongside the remarkable means of machine learning into their manufacturing sector, changing the very core of industrial production. Moreover, the ability of CNC machines to self-correct issues and reroute processes in real time has drastically lowered the amounts of required human oversight. This has produced remarkably efficient results and vastly increased the pace of production.
The incorporation of 5 axis CNC machining systems has propelled the advancement of precision engineering as we once knew it. In comparison to 3 axis systems which only permit linear guided movements, 5 axis machines are able to move the tool in 5 different directional axes which permits the crafting of highly detailed and precise components for the medical and aerospace industries.
Analyzing recent research, it becomes clear that the worldwide market of CNC machines is predicted to experience a consistent increase of 7.7% annually from 2021 to 2028, surpassing $132 billion in the latter year. This demonstrates the market’s desire for technologies that enhance productivity while retaining accuracy. In addition, advancements in CNC machining technologies like the machining of composites and superalloys have broadened the employs of CNC machining, enabling it to tackle more complex and diverse production challenges.
With greater adoption of IoT technologies and connectivity, CNC systems have integrated into smart manufacturing ecosystems, enabling remote supervision and collaboration with other automated systems, so that streamlined operations across different production lines can be performed. These innovations mark the enduring advancement of numerous technologies within the industry and highlight the profound impact of CNC machining in contemporary civilization.
Fundamental aspects of the working of a CNC machine
CNC machines are a product of modern technologies that maximized precision, speed, and efficiency of operations. One of the fundamental processes among them is tool path optimization, which helps in reducing the idle time of the machine as well as unwanted tool movements. The most recent technological development within CNC produced rotary tools involves adaptive machining and real-time adjustments for material properties and tool wear, which dramatically minimizes error and waste in production.
The global CNC machine industry is worth an estimated $84 billion and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.5% from 2023 to 2030. The industry report cites the automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors as primary drivers of this growth due to their increased demand for customization and precision.
Predictive maintenance is possible due to the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into CNC systems. By evaluating performance data, these systems can anticipate issues, alleviating up to 20% of downtime. This enhances machine dependability and improves strategic resource allocation.
Furthermore, advanced cutting tools polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and cubic boron nitride (CBN) have been manufactured to work with more difficult materials such as composites and alloys. Together with sophisticated CNC software, these tools guarantee the maintenance of quality standards in complex and demanding production settings.
Advancements of CNC Technology in the Manufacturing Process
In my opinion, the evolution of CNC technology has transformed the manufacturing process with regard to precision, efficiency and flexibility. CNC systems were only capable of executing simple tasks at first, but they have now progressed to highly complex and precise designs. Today, CNC machines are capable of integrating AI, IoT, and even predictive analytics for autonomous supervision, real-time analysis, and decision-making. Remarkably, now productivity can be pursued to unprecedented levels without sacrificing quality. This is all possible with effortless complex project undertakings.
What are the 5 most common types of CNC machines?
- CNC Milling Machines – These are used for cutting or shaping of different materials with rotating cutting tools.
- CNC Lathes – Known for producing cylindrical sections through rotation of the workpiece against cutting tools.
- CNC Plasma Cutters – Cut metals and other conductors with a plasma torch at extremely high temperature.
- CNC Laser Cutters – Cut or engrave various materials with a focused laser beam.
- CNC Routers – Best suited for the cutting, carving and shaping of wood, plastic, foam and other soft materials.
- CNC Routers – Best suited for the cutting, carving and shaping of wood, plastic, foam and other soft materials.
CNC Milling Machines: Capabilities and Applications
Every business has a purpose, which is why CNC milling machines are versatile to cater for businesses in need of precision manufacturing. These machines work by removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutting tools which means these machines can perform numerous tasks such as drills, carving, and contouring. Modern CNC milling machines can operate on many materials, metal, plastic and composites, to satisfy production requirements.
The precise measurements attainable by CNC milling machines is a notable strength. Depending on the specifications of the machine, tolerances of ±0.0001 inches can be achieved, which is crucial for aerospace and medical device manufacturing. Furthermore, 5-axis multi CNC milling machines can perform more intricate tasks than their predecessors, increasing their versatility and usefulness.
The global CNC machine market was valued at approximately $83.99 billion in 2022. It is expected to have a CAGR growth of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030 – this encompassing other segments in the industry too. CNC milling machines have a large portion of this value due to their demand in the auto, electronics, and defense industries, needing accurate parts.
The AI-powered automation features allow for remote monitoring, adaptive control, and real-time interfaces with IOT devices. Everything mesh together to help refine the production process. These factors are what burnish the reputation of the these machines. Automating processes allows for minimal waste and time while keeping a steady quality of the output.
CNC Lathe Machines for Turning Operations
CNC lathe and turning machines are very accurate precision tools designed for turning processes where a workpiece is spun as a cutting tool modifies its configuration. Because of their ability to make sytemmetrical parts at a high speed, these machines are very important in aerospace, defense, and automotive industries. CNC lathe and turning machines are now capable of more elaborate geometries as well as multi-step machining processes in one setup owing to new advancements like multi-axis features as well as live tooling.
The CNC lathe market is analyzed to increase with a CAGR of 5.8% between 2021 and 2028, mostly due to the growing CNC lathe demand because of automation in manufacturing. The turning processes also undergo transformation due to new hybrid CNC lathes that incorporate additive manufacturing. These hybrid CNC lathes transform standard cnc machining processes by decreasing the time required for production and improving material usage. New CNC lathe and CNC turning machines are innovative because of their IoT connectivity which enables real time data tracking and predictive maintenance, providing consistent quality and efficiency simultaneously.
CNC Routers for Woodworking and Other Materials
The woodworking sector has been transformed by CNC routers, as they are more efficient and multifunctional than the hand tools. The computer-controlled devices are specialized in cutting, carving, engraving, and shaping workpieces made out of wood, plastics, foams, and even some metals like aluminum. The most recent data shows that with software integration and multi-axis capabilities, CNC routers can now accurately produce intricate designs with more than 30 percent material savings when compared to traditional methods.
Another important development is the widespread adoption of spindles with high torque which allow faster cuts to be made without reduction in quality. Some of the more advanced types of CNC routers will even exceed 24,000 RPM, making the machines ideal for parts production work. In addition, the new systems that use vacuum tables make the hold-down of the materials quicker and more reliable.
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, CNC routers now have the capacity for real-time operational data tracking and optimization, monitoring tool wear and power consumption, as well as production output with detailed precision. Such advancements enable manufacturers to automate maintenance scheduling and decrease operational interruptions. As per estimates, by 2025, the global CNC router market is expected to expand at 5.7% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) owing to heightened demand from the furniture industry and signage manufacturers.
Advancements in CNC Plasma Cutting Machines for Sheet Metal
The precision, flexibility, and economic efficiency of CNC plasma cutting machines have made them popular in the sheet metal work industry. A CNC plasma cutter employs a plasma torch to slice through metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper, propelling them at high speeds. This technology is largely used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment manufacturing industries.
Further CNC plasma cutters provide additional features. Enhancements made to the integration of software systems enable more effective control of cutting patterns which improves material saving capabilities by almost 30%. More recent model plasma torches also improved cutting speed by nearly 15% when compared to previous models. The improvement is extremely useful in time sensitive bulk production scenarios.
The rise of smart manufacturing is driving the market trends for an automated plasma cutting system. As per an industry report, the overall market for CNC plasma cutting devices is projected to expand at a CAGR of approximately 6.2% until 2028, on account of the adoption of Industry 4.0. There is a mounting IoT sensor-enabled feedback system on these machines. Sensors feedback in real-time on performance indicators like arc voltage and cutting temperature, which further enhances efficiency and consistency while lowering downtime.
In addition, the latest advancements in the environmental technology sector focus on creating plasma systems that have reduced emissions as well as enhanced energy efficiency. Equipment with up to 20% lower energy consumption is offered by select providers, Improving productivity while meeting growing demands for sustainability during operation.
These developments in technology are strengthening the position of CNC plasma cutting machines as an indispensable asset in metal fabrication, arming manufacturers to address the sophisticated challenges of modern production.
Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM) in CNC Manufacturing
Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM ) provides CNC manufacturing functionality in precision and intricate gold metal plating detailing. EDM processes utilize electrical sparks to erode the material and complex geometries which traditional machining aren’t able to achieve. This is beneficial in hard materials like titanium, tungsten and hardened steel.
Technology related to EDM processes have become increasingly accurate and efficient over the years. For example, recent research indicates that the use of AI algorithms into the ECM systems can achieves accuracy increases up to 30% when compared to previous methods with lower tool loss. Also reduction of up to 40% in new developments of dielectric fluids innovations lead to more sustainable practices to put into place in a stronger world. Consistently tight tolerances along with high repeatability make EDM an undeniable indispensable answer for companies in the aerospace automotive and even medical instruments industries.
How do different CNC machine types compare in performance?
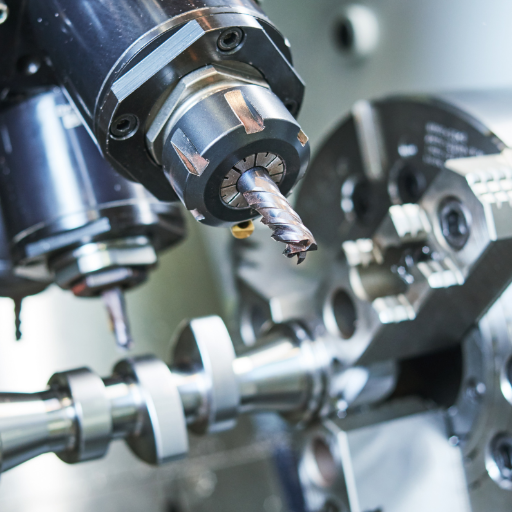

The difference between CNC machines lies in their efficiency as a result of the design and application of the particular type. Horizontal CNC machines have more stability and are better suited for bulky, heavy components while vertical CNC machines are more versatile and better suited for smaller parts and more detailed work. Multi-axis CNC machines, like for example the 5-axis models, are well-known for performing complex cuts with precision at many angles in one setup, which is often needed in delicate jobs for aerospace. As always, the correct choice is dictated by the specific machining operations, material, and the precision level provided.
3-axis vs. 5-axis CNC: Which Type Offers Better Precision?
With regards to 3-axis and 5-axis CNCs, the precision is not the same and largely relies on the complexity of the part and the machining demands. The 3-axis machine operates in three linear dimensions (moves in X Y and Z directions), which makes it the perfect match for simple parts. This type of machine is particularly good when milling, drilling, or cutting flat and symmetrical objects. Because of the linear movement, though, 3-axis machines may perform multiple setups to achieve accurate angles on more complex parts, which in turn can lead to small accuracy errors.
In the case of 5-axis CNC machines, a cutting tool, or a workpiece is able to tilt and rotate, thanks to the two additional rotational axes. This alteration can improve access to complex and curved surfaces without the need for repositioning and by canceling the need for repositioning. Some parts of the industry, like gas turbine engines and medical devices, are highly specialized and their components need to be manufactured with extreme precision. 5-axis machines eliminate the need for manual intervention during pre-set tasks to significantly improve precision and automate human-less repetitive work. Other studies also show that automation with 5-axis machines can save production time by 20-30% due to less rigid workflows and reduced operational blockages.
While 3-axis machines remain more affordable and easier to procure, precision work favors the 5-axis machine, as it propels advanced capabilities into the limelight. The combination of these two axes shifts the reasoning for the balance of cost and functions between the applications to be made and the tolerances to be required.
Analyzing CNC Lathes and CNC Mills for Particular Purposes
While both CNC lathes and CNC mills perform automated and accurate machining, they differ with respect to their areas of application. Specifically, CNC lathes are optimal for the production of symmetrical cylindrical parts, which include shafts, bushings, and fittings. Lathes excel in operations like turning, threading, and boring, where they utilize rotational motion to engrave high-precision geometry at an unprecedented rate. For instance, one study reported that CNC lathes can outperform manual setups by as much as 20% in speed for small cylindrical components, subsequently lessening production costs in mass manufacturing.
Conversely, CNC mills are best suited for projects that have intricate outlines having various intricate indentations such as slots and holes and angled cuts. Mills are equipped with multi-axis rotation and are thus able to carve out materials in a 3D shape, adding detail to the part, hence why they are used for prototyping and manufacturing of medium to low quantities of intricate parts. Research suggests that modern 5-axis mills, widely utilized in the aerospace and medical manufacturing sectors, are more efficient for material utilization by 15-30% compared to older, less sophisticated machines.
Using a CNC lathe versus a CNC mill largely depends on overarching factors like design intricacy, tolerances, and volume of production. Take the example of creating a cylindrical drive shaft: it would conventionally be much more affordable to produce it with a lathe. Meanwhile, a part with pockets and multi contour surfaces would be better served on a mill due to its versatility. Both pieces of equipment have a place in precision machining and ergonomically work together in a production setting.
CNC Laser Cutters vs CNC Plasma Cutters : Key Differences Explained
When it comes to CNC laser and plasma cutting, the two tools are multifunctional within the realm of precision cutting; however, each has its specific material and area of application. The primary difference lies in the cutting method. Chipboard, hardwood, aluminum, thin sheets of thick metals, plastics (polystyrene), wood glass, and many other items can be cut with great detail and heat by CNC laser cutters as they melt or vaporize the material using focused beams of light.
CNC plasma cutters work by ionizing a gas to produce a plasma arc that cuts through materials like steels, aluminum, and copper. Plasma cutters are preferred in industrial construction and automobile manufacturing because of their efficiency in cutting thicker metals since robust cutting capability is typically needed in industrial applications.
Regarding operational costs, maintenance on CNC laser cutters may be more expensive due to the complexity concerning laser technology. On the other hand, costs associated with energy consumption may be lower, as CNC laser cutters are more efficient with energy on some materials. Furthermore, because of how clean the cuts are, post-processing becomes unnecessary. Compared to CNC laser cutters, CNC plasma cutters have lower operational costs, and while they are faster when cutting thicker materials, the additional finishing required for precise applications increases operational costs.
As an example, a standard CNC industrial laser cutter can cut with a precision of ±0.001 inches, whereas a plasma cutter achieves a tolerance of ±0.01 to ±0.03 inches depending on the setup. In addition, on thinner materials laser cutters routinely attain cutting speeds ranging from 20 to 70 inches per minute, while the plasma unit is superior in cutting speed on heavy and thick metals. The selection of one over the other is mostly determined by the material to be worked on, the intended accuracy, and the purpose of use.
Which type of CNC machine is best for specific applications?
- Laser cutters excel at cutting thin materials like wood, acrylic, and certain metals with high precision and a clean finish.
- In construction and fabrication industries, plasma cutters are better suited for quickly cutting thick metals.
- Milling machines specialize in creating complex parts and detailed 3D shapes from metal or plastic.
- Lathes are essential for parts that are cylindrical in nature such as shafts and pipes, which require rotational symmetry.
Performance Factors of CNC Machines in Metal Fabrication
Performance and productivity of CNC machines used in metal fabrication are influenced by precision of the machine, the properties of the material, the cutting speed, and the type of tool utilized. One key area of focus is spindle speed, which has a direct impact on quality and productivity of the machining work done. Utilizing high spindle speed works best with softer metals like aluminum, while harder metals like steel need reduced speeds to avoid excessive wear on the tool and maintain fine details.
Ultimately, all these factors combined have significant implications on the overall accuracy required for a given task. Furthermore, while optimizing the strategy, it is important to have clear expectations about the end results to guide each step taken. CNC machines now boast cutting speeds reaching a staggering 1,000 inches per minute while maintaining an impressive tolerance of ±0.001 inches. This is often seen with modern machines and their growing versatility durable with different tasks.
In terms of the upload and input side, new revisions to the CNC programming have greatly positioned the level of automation. Particularly, intricate designs not only can but can easily be executed without active manual labor. Moreover, contemporary capabilities enable active monitoring alongside other tasks which enhances workflow proportionally while minimizing costly mistakes. Therefore, together specific parameters of the machine alongside its features programming guarantees maximum efficiency.
Best CNC Machines for Woodworking Projects
For precision CNC woodworking equipment, details like accuracy, speed of cut, and versatility with different materials are extremely important. CNC machines for woodworking possess capabilities such as cutting, carving, drilling, and engraving. High spindle speed machines, defined as those operating between 18,000 and 24,000rpm, are critical for softwood and detailed engineering cutting to achieve clean, precise cuts. In addition to this, multi-axis features (3-axis or 5-axis) greatly aid in the fast and efficient detailed 3D carving with the reduced risk of having to reposition the material multiple times.
Good woodworking CNC machines must integrate strong dust collection systems for precision work and operator safety. More advanced machines, such as ATC routers, have more complex productivity enabling features such as seamless tool type transitions. More recently, CNC routers with servo motor systems have been proven to outperform their stepper motor counterparts when it comes to precision and reliability in high speed CNC cutting.
With the right software like Vectric Aspire and Fusion 360, these machines are capable of turning digital designs into physical objects with great precision. For small workshops, reasonably priced compact desktop CNC routers with sufficient power and easy-to-use interfaces give small businesses an affordable means to achieve professional-grade results. These developments further emphasize the need to carefully choose tailored CNC machines that best address specific woodworking requirements.
Popular types of CNC machines for small machine shops
- CNC Routers: Best for engraving, carving, cutting, and shaping wood, plastic, or soft metals. Widely used in furniture fabrication, sign making, and intricate patterning.
- CNC Milling Machines: Best for mechanical cutting and drilling into various materials including metals and plastics. Smaller sized variants are appropriate for small machine shops.
- CNC Laser Cutters: Engraving and cutting of thin materials like acrylic, wood, and fabric is done with great precision, speed and is mess-free.
- CNC Lathes: For rounding operations, CNC Lathes are best suited for table legs, handles, and other round decorative objects.
How to choose the right CNC machine for your needs?
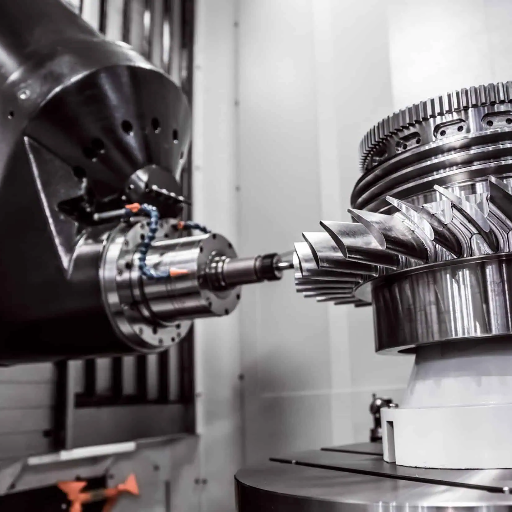

- Type of Material: Identify the base materials to be worked on e.g. wood, metal, plastic and select a machine tailor-made to those materials.
- Intended Use: List down particular actions you wish to perform using the machine: cutting, engraving, turning, etc. Then, select the appropriate machine.
- Size and Workspace: Consider the available space in your workshop to ensure that the machine does not hinder safety or efficiency practices.
- Budget: Consider the purchase price of the machine alongside its maintenance, tooling, and operational expenses.
- Ease of Use: For smaller operations, select a machine with simple controls.
Advancements in CNC Machine Technology
In modern times, precision, efficiency, and adaptability offered across different fields have seen a boost with the help of new advancements CNC machines receive. Such modern systems now come with extra capabilities like AI automation, real-time monitoring, and IoT connections. As stated in one of the reports, the CNC machine market is anticipated to have a 5.5% CAGR from 2023 until 2030. This is attributed to the growth in automation within production lines as well as the rising acceptance of Industry 4.0.
The newest CNC technologies enable multi-axis configurations to scale from 3 to 9 axes, allowing for the more intricate and precise fabrication of components. An example of this is in the aerospace and automotive industries where 5-axis CNC machines are widely utilized due to the need for sophisticated shapes and demanding material tolerance. There is also a rise in the market for hybrid CNC machines that add an extra dimension of flexibility by combining additive manufacturing with traditional CNC machining. Hyper-accurate subtractive and additive manufacturing processes can now be executed in one device setup (Fusion3D™).
Workflow-dominated industries also benefit from the optimized energy and toolpath designs recent CNC technologies have to offer. Improved programming can, for example, reduce machining time by up to 30% while also decreasing material consumption, greatly reducing the costs associated with operating the machine. Together with the other advancements, these changes demonstrate how CNC machines are made more capable and versatile to address the needs of modern day industrial societies.
Cost Analysis of Various Types of CNC Machines
In the cost assessment of different types of CNC machines, the immediate purchase pricing, as well as the subsequent operational costs should be taken into consideration. Entry-level machines such as desktop milling machines usually retail between $1,000 and $5,000, making them easily accessible to hobbyists and small businesses as they offer basic functions at a lower price. 3-axis CNC routers, on the other hand, fall under mid-range category, offering better precision and flexibility ideal for commercial use. They are priced between $5,000 and $50,000.
5-axis machining centers and CNC lathes are examples of high end industrial CNC machines which cost $50,000 to more than hundreds of thousands of dollars. These machines make intricate parts with outstanding precision, so they are priced higher. They are built for mass production.
Per unit, an industrial-grade CNC machine may have a higher power consumption, but due to increased efficiency in material consumption and output, the overall cost per unit is lower. For example, the type of machinery used has a great impact on power consumption, maintenance, and tooling costs. Software functions, automation, and features also impose impact on these costs, giving manufacturers the option to customize the solutions according to their needs.
How New Technologies Impact the CNC Industry
Efficiency, precision, and flexibility are key areas in need of advancement in technology, and CNC is no exception. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) make up the most significant emerging trend in the industry. Using these technologies, CNC machines can now self-optimize, schedule maintenance, and predict downtime. AI has reportedly boosted process optimization by 30% along with a reduction of waste material which enhances productivity overall.
No less revolutionary is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into CNC systems. CNC machines embedded with IoT capabilities enhance remote monitoring and control and enable the collection of critical data like cycle times, tool temperatures, and performance metrics. A recent study suggests that businesses adopting IoT to CNC machinery experience a 15% increase in efficiency in operations.
Moreover, the several advancements with multi axis machining are broadening the production scope for complex geometry and intricate components. 5 and even 6 axis machines can make smoother and faster, higher quality cuts enabling faster production turn around times of critical components. This is exceptionally useful in the aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries.
Finally, the design and manufacturing of components undergo a transformation with the advent of hybrid machines which integrate CNC milling and 3D printing. Highly customized parts can be created with precision and material wastage is significantly reduced, making it an appealing choice for environmentally sustainable companies.
These changes are preparing the groundwork towards the next level of growth in CNC technology and help manufacturers keep pace in a fast-advancing world.
Reference sources
- Study: The Link and Match Between the Competency of Vocational High Schools Graduates and the Industry on CAD/CAM and CNC1
- Objective: To analyze the alignment between vocational education competencies and industry requirements in CAD, CAM, and CNC operations.
- Methodology: The study employed a descriptive-qualitative approach, involving interviews and observations with industry professionals and vocational school educators.
- Key Findings:
- The study identified four key competencies required in the industry: setting CNC machines, operating CNC machines, CAD drafting, and CAM programming.
- CNC operators performed tasks such as setting zero points, editing program codes, and operating machines, while CAD drafters and CAM programmers focused on design and programming.
- The research highlighted gaps between vocational training and industry needs, emphasizing the importance of advanced CNC training, including multi-axis operations, to meet modern manufacturing demands.
- Study: Automated Generation of CNC Programs for Manufacturing: A Review4
- Objective: To explore methods for automating CNC program generation to enhance efficiency and accuracy in manufacturing.
- Methodology: The study reviewed parametric design and configuration systems for CNC programming, focusing on CAD/CAM integration and G-code automation.
- Key Findings:
- Automated CNC programming can significantly reduce production time and costs while ensuring high precision.
- The study introduced a decision tree for selecting appropriate programming approaches, such as CAD/CAM or parametric programming, based on product complexity.
- It emphasized the need for further research to overcome limitations in automating CNC programming, particularly for complex geometries.
- Top ATC CNC Router Manufacturer And Supplier In China
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of CNC machines commonly used in manufacturing?
A: In manufacturing, the five most frequently used CNC machines are CNC mills, CNC lathes (turning machines), CNC routers, CNC laser cutting machines, and CNC plasma cutters. Each machine tool serves specific purposes in manufacturing. They also have a diverse list of compatible materials, like mills and routers, which pseudo-embroider textiles and paper crafts to block materials touch while lathes, plasma and laser cutters glide along metal and plastic. CNC mills and lathes specialize in precise work. However, with CNC routers, cutting woods and plastics with the utmost finesse as laser cutters do on broader yet thin sheets, yields flawless quality. It is also widely known that CNC grinding machines, CNC water jet cutting units, and CNC EDMs gained equal popularity in their own rights.
Q: Which types of CNC machines are best for precision manufacturing?
A: Generally, CNC mills and CNC lathes take lead to precision CNC machining the fastest. However, CNC grinding machines deliver outstanding reliability in finishing tasks. Some even go as low as 0.0001 inches worth of tolerance while claiming it was not nanometer sufficiency. Etching pliers beat the rest where timeliness and details need to be burdened with extreme intricacies – – like fixing stencils out of hard materials, not soft ones. Anything out of sheets gets their engrave laser cut. On the contrary, when undergoing precision tasks, absolute work may be judged on the intended use and material graces itself in the ever-reliable tolerance invaluable to users.
Q: What are the 5 different types of CNC milling machines?
A: The five different types of CNC milling machines include: 1) Vertical mills wherein spindles are oriented vertically for face milling and drilling operations, 2) Horizontal mills with horizontal spindles that are ideal for heavy cutting and large workpieces, 3) Universal mills which can operate both vertically and horizontally, 4) Multi axes mills (5 axis or more for complex geometries), and 5) Bed mills which have a fixed table and moving cutting head. Each of these types vary in the amount of efficiency with which they use CNC technology for material removal and in meeting various manufacturing needs.
Q: What do industry experts consider as the best starting CNC machine?
A: Industry experts suggest that CNC routers are the most recommended starting machines for new users. These machines cost less than other types and have a simple learning curve. Additionally, they can work with a variety of materials such as wood, plastics, and other soft metals. Compared to intricate systems like 5-axis mills or CNC grinders, entry-level CNC routers are a lot easier to operate and require less technical expertise.
Another suitable option for learners in metal working is desktop CNC mills. More experienced users can later shift to more complex devices such as CNC lathes or sophisticated multi-axis milling centers.
Q: What differentiates CNC grinding machines from other common CNC devices?
A: Unlike other common CNC machines, CNC grinders CNC use abrasive wheels instead of cutting tools. CNC mills and lathes are different from CNC grinders since they use blades to remove block sections of material, while CNC grinders make incremental changes using countless small abrasive particles. CNC grinders are usually used for finishing touches that are required to have very precise measurements and outstanding quality finishes. Other types are: surface grinders, cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, and tool and cutter grinders. These machines are greatly advanced and are required for processes which have extremely critical dimensional requirements and cannot be done with conventional machining.
Q: For which purposes, CNC water jet cutting machines have their primary applications?
A: The greatest use of water jet cutting machines by CNC is for cutting stone, metal, glass, demanding composites as well as thick and hard ceramic materials. These machines can also effortlessly perform complex designs. The CNC water jet cutter is increasingly being utilized in aerospace, automotive and architectural businesses due to its unparalleled accuracy and precision in 3D precise model cutting. Unlike cutting laser or other heat-consuming devices, CNC water jet machines do not bring any adverse effects or areas disturbed by heat (HAZ) during or before the cut.
Q: In what way do various types of CNC laser cutting machines differ in their performance?
A: Various types of laser cutting CNC machines differ in their abilities and productivity: for nonmetals and some metals, CO₂ lasers are multifunctional; fiber lasers have greater cutting speed for reflective metals; thick materials are cut more efficiently with crystal lasers (Nd:YAG); and energy-efficient direct diode lasers. Performance is influenced by power (150W to 6kW+), cutting speed (typically 2-3 times faster for thin metal with CO2 compared to fiber lasers), precision (±0.1mm), and compatibility. More advanced systems feature auto-focus, material detection, and sophisticated nesting algorithms which sharpen material consumption. The system configured best for your needs is what will serve you best.
Q: What other new CNC technologies are there aside from the 5 common types of CNC machines?
A: Other than the common CNC machines, new CNC technologies include: hybrid machines featuring 3D printing and subtractive machining in one system, ultra-high precision microparts machining centers working at sub-micron accuracy, CNC systems with AI and adaptive machining learning capabilities, robotic integrated CNC cells that automate multiple processes, and multi-laser metal 3D printers for more complicated shapes. Additionally, rotary axis wire EDM, multi 7+ axis machining centers, and intelligent CNC grinders with in-process measurement are also advancing the limits of manufacturing processes. These are advancements in the world of CNC manufacturing technology that enable the creation of complex manufactured parts at a higher efficiency than before.
- Pulse vs Beam vs Burst Lasers: Continuous Weapon Comparison?
- Buying a Cheap Laser Cutter: Pros and Cons of Budget Laser Machines
- The Complete Laser Cutter Buying Guide: Choosing the Best Laser for Your Needs
- Laser Dental Cleaning vs Traditional Methods: Revolutionizing Dentistry with Laser Teeth Cleaning
- The Ultimate Guide to Laser Surface Cleaning Safety: Protecting Yourself While Using a Laser Cleaner
- Discover the Power of UV Laser Marking Machines for Precision and Versatility
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Your First CNC Machine for Home Workshop
- Laser Cleaning: Advantages & Disadvantages of the Machine

